Off Page SEO checklist: What It Is and Why It’s Important, A complete guide
Off Page SEO checklist
Struggling to rank in Google despite pouring your heart and soul into your content? Your off-page SEO—or lack thereof—may be the culprit.
SEO can be divided into two buckets: on-page SEO and off-page SEO.
Many see off-page SEO as synonymous with link building, but is that really the case?
What is off-page SEO?
Off-page SEO embodies any efforts taken outside of a website to improve its search engine rankings.
Link building is a big part of this, but it goes way beyond that.
On-page SEO vs. off-page SEO
On-page SEO is something you have complete and utter control over, whereas that’s not always the case for off-page SEO.
For example, if I reach out and ask someone to link to me, that’s off-page SEO. Why? Because I didn’t change anything about my website during that process. Conversely, if I improve my page speed by optimizing some images, then that’s on-page SEO because I made that change directly on my website.
If you’re ever confused as to which “bucket” an SEO tactic falls into, ask yourself whether it’s entirely within your control. If the answer is no, then it’s most likely an off-page SEO tactic.SIDENOTE. There are some off-page factors that you have complete control over (e.g., Google My Business).
Why is off-page SEO important?
Google takes into account many off-page factors when deciding if and where to rank web pages. Links are one of those factors, but there are many others.
For that reason, it’s challenging to rank on the merit of your content alone.
Here’s a good example that proves this:
At the time of writing, this page from The Times ranks #1 in the UK for “best places to live”:

At first glance, it looks like an entirely worthy piece of content. So it wouldn’t be crazy to assume that it ranks high for that very reason. However, as soon as you click on any of the places, you hit a content gate.
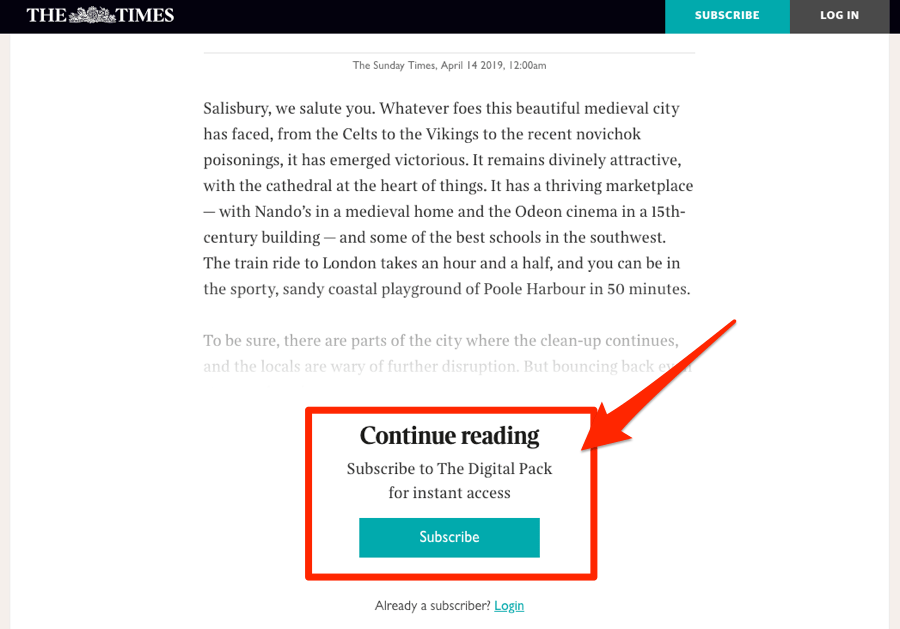
Because of this, the page has no real value to most who land on it… and it certainly doesn’t deserve to rank in the top spot.
A much more deserving page would be this one, which showcases the results of polling 1,000 people about the best places to live.
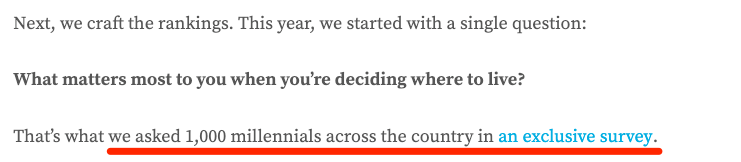
Bringing this back to off-page SEO, the reason the former outranks the latter is not that the content is better but most likely due to off-page factors.
[amazon box=”B084LF85PC” “small”]
Link-related off-page factors
Backlinks are perhaps the most critical part of off-page SEO.
Why? Because Google search is built on something called PageRank: an algorithm that looks at the quantity and quality of backlinks pointing to a web page. Some SEO professionals see PageRank as an outdated concept, but Google confirmed that it’s still a ranking factor only last year.
That’s likely why we see such a clear correlation between the number of referring domains (unique websites) pointing to a web page and its rankings.
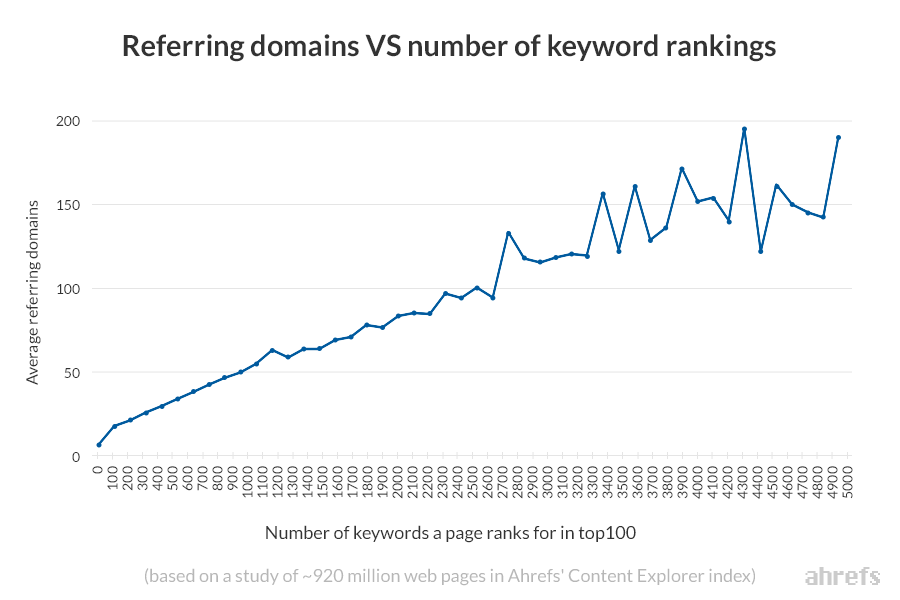
…which brings us neatly onto our list of link-related off-page factors:
Also read : how to do Keyword research And ultimate guide to robots.txt
Off Page SEO checklist
1. Number of referring domains
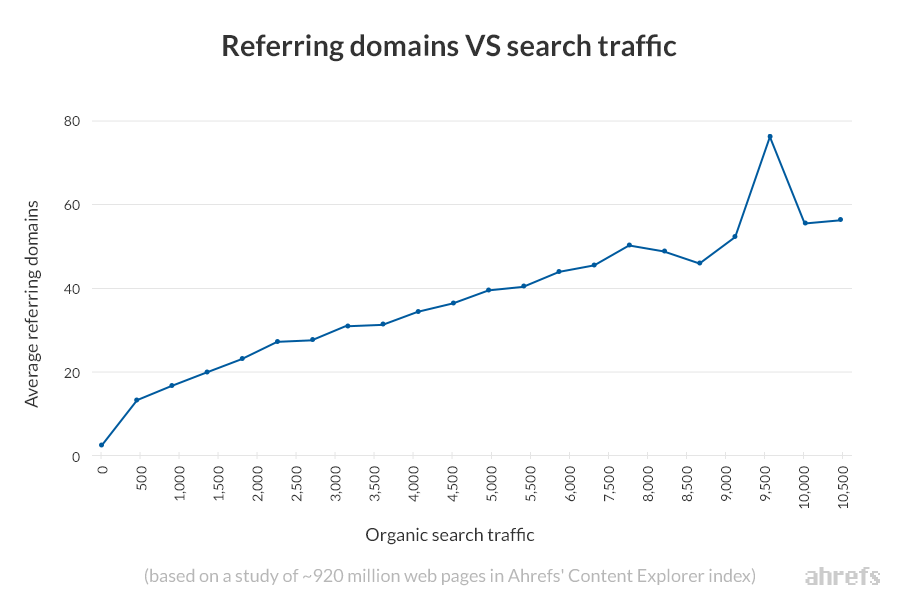
Not only does having more links from unique websites (referring domains) equate to higher rankings, but also more organic search traffic.
To check how many backlinks your website has, paste your domain into Ahrefs’ Site Explorer or our free backlink checker.
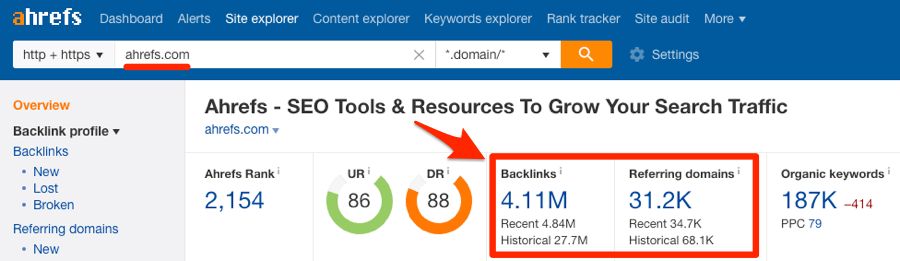
You can see that ahrefs.com has 4.11M backlinks from 31.2K referring domains.
However, the aim isn’t so much to build more backlinks to your website overall, but rather to build them directly to the pages you want to rank in search engines.
We have tons of articles and videos on building more links. See below.
FURTHER READING
- EASY Link Building Strategies (That ANYONE Can Use)
- How to Get Backlinks: Tactics That Don’t Require New Content
Also read : Seo top keyword reasearch tools And Long tail keywords complete guide
And secrets of article writing
and what is page speed and total guide and what is follow links
2. Link authority
Not all links are created equal. Quality matters.
This fact is built into the way PageRank works. The higher the “authority” of the linking page, the more authority it passes onto the pages to which it links. In other words, a link from a high-authority page is worth more than one from a low-authority page.
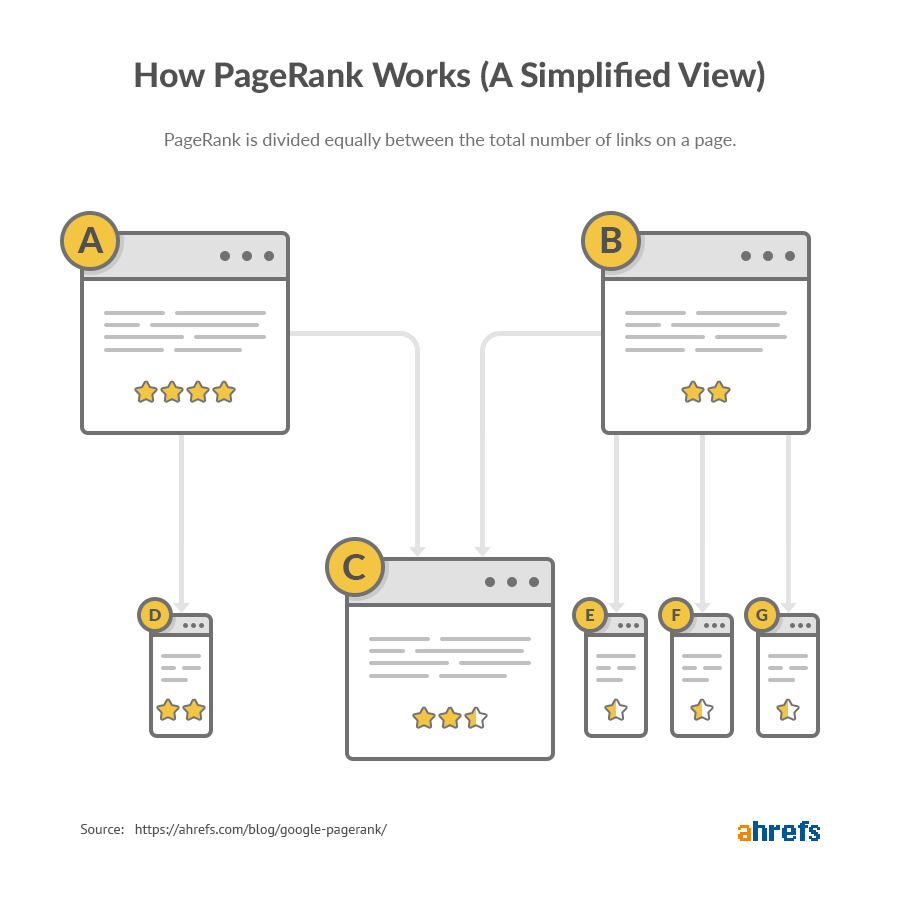
So the question is, how do you judge the “authority” of a web page?
Google used to have public PageRank scores, but they discontinued those in 2016. While no exact replica of PageRank exists, there are a few similar metrics around, one of which is Ahrefs’ URL Rating (UR).
UR shows the strength of a target URLs backlink profile on a scale from 0 to 100.
To see the UR score for any web page, paste the URL into Ahrefs Site Explorer.
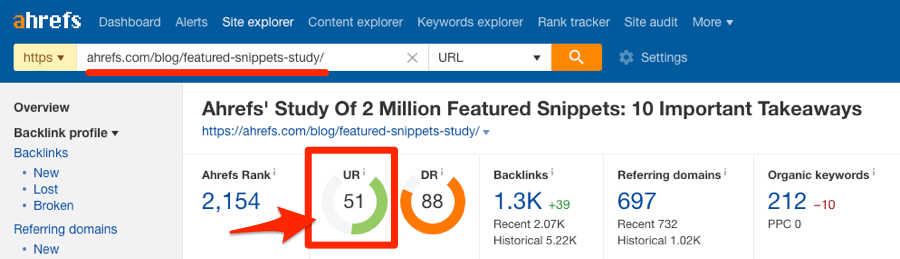
You can also see the URL Rating of all referring pages in the “Backlinks” report.
This helps judge the quality and authority of a linking page when researching backlink opportunities.
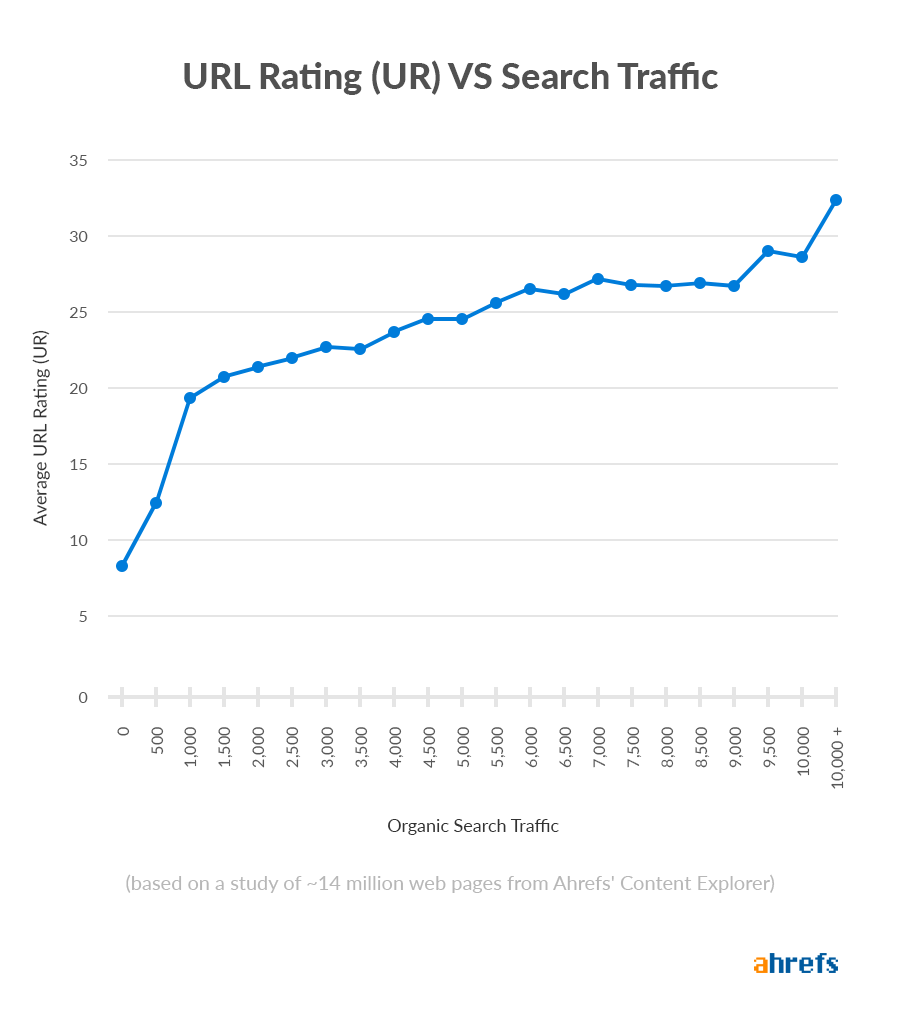
Plus, according to our study of ~14 million web pages, UR correlates nicely with organic traffic.
3. “Dofollow” vs. nofollow : Off Page SEO checklist
Google doesn’t transfer PageRank across nofollowed links (i.e., links with a rel=“nofollow” tag), so it pays to prioritize the building of followed (“dofollow”) links.
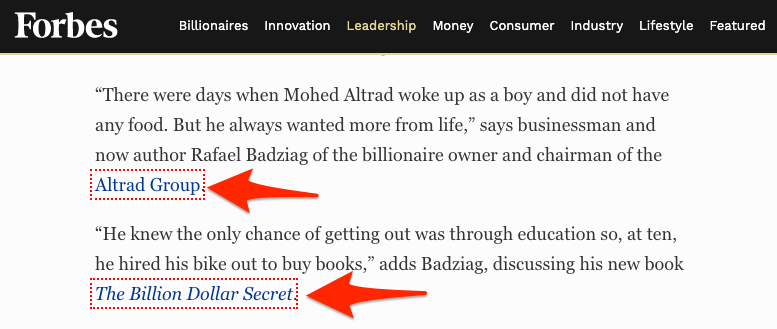
Most links on the web are followed, but some websites like Forbes “nofollow” almost all outbound links. So, if you’re actively building or pursuing links from a particular website, it pays to make sure that their outbound links are followed.
To do this, install the nofollow Chrome extension, which highlights nofollow links on the page.
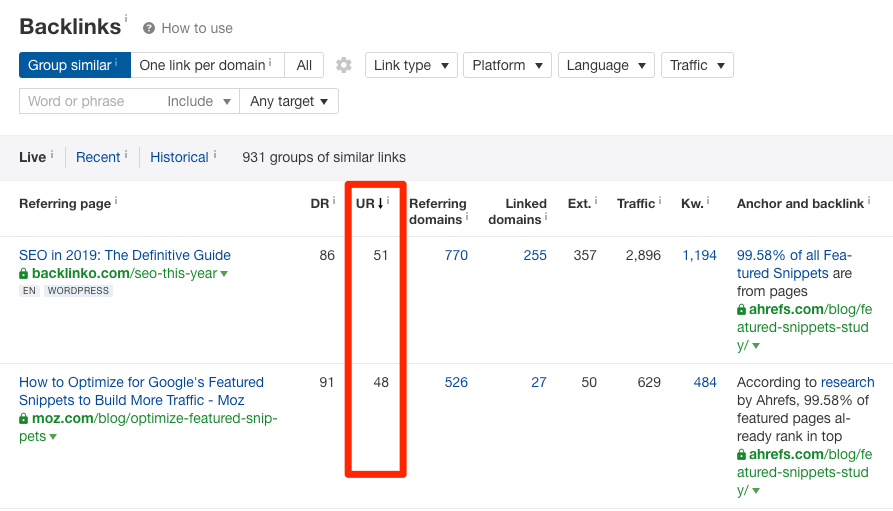
You can also filter many of the reports in Ahrefs Site Explorer to see only “dofollow” links. Once again, this is useful when researching and prioritizing backlink opportunities.
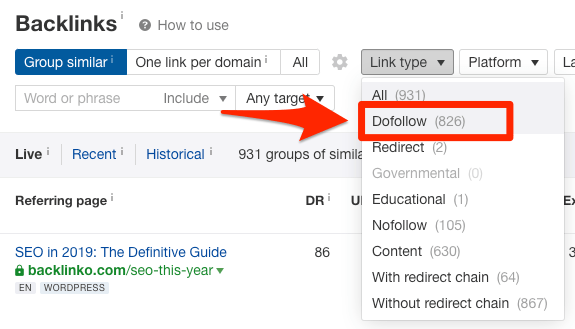
Filtering the “Backlinks” report in Ahrefs Site Explorer for “Dofollow” links only.
Of course, there’s still value in nofollowed links. They can drive referral traffic, which can have a positive indirect effect on SEO. But if you’re putting a lot of time and effort into link building, then it pays to prioritize your efforts.
Also Read :Complete SEO checklist And How to install google analytics
4. Anchor text : Off Page SEO checklist
Anchor text refers to the clickable words used to link one web page to another.
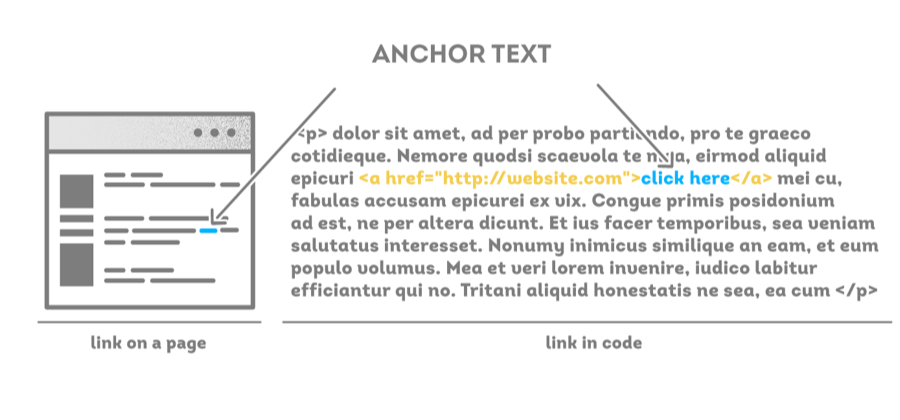
Google states in their original PageRank patent that:Google employs a number of techniques to improve search quality including page rank, anchor text, and proximity information.
In other words, it’s likely that backlinks with anchor text relating to the overall topic of your web page have some influence on rankings.
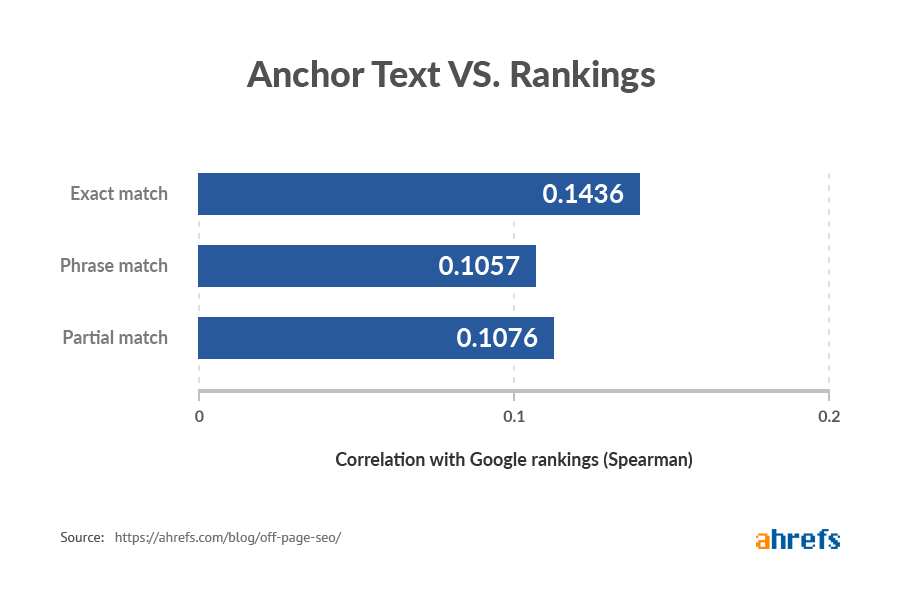
This is something we studied, and we did find a correlation between exact, phrase, and partial match anchors—albeit a very small one.
Unfortunately, if you’re building links via white-hat methods, you won’t have much control over the anchors of the links you’re earning (with the exception of guest blogging).
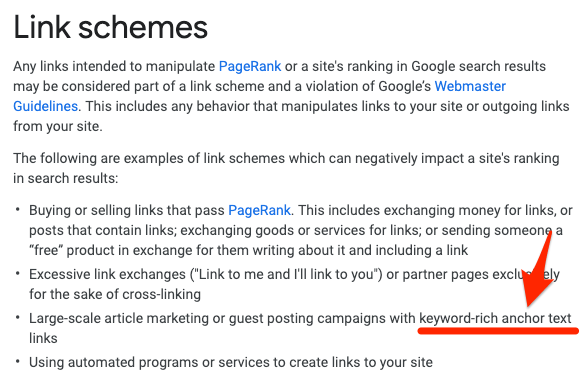
But even if you did have control over the anchor text of external inbound links, it’s possible to have too much of a good thing. Penguin—which is now part of Google’s core algorithm—penalizes sites that attempt to manipulate rankings by building links with keyword-rich anchors.
Luckily, most people naturally link in natural and relevant ways. If your article is about x, then the chances of someone linking with anchor text related to x is quite high.
Diversify anchor texts: After conducting a full backlink analysis and seeing where your links are coming from, you should next work to diversify your anchor texts.
Diversifying your anchor texts simply means using different keyword phrases, brand names, and generic terms so that Google will view your links as natural and not manipulative.
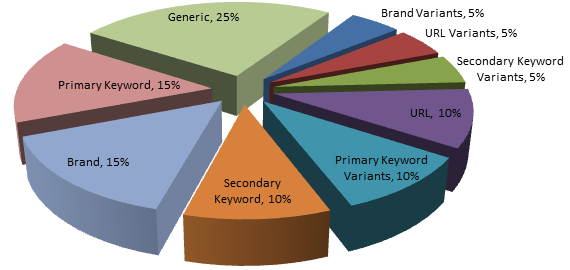
After all, if you didn’t do anything fishy to get the links, then your links shouldn’t all have exact match keywords in their anchor texts, right?
When diversifying your anchor texts, make relevance your top priority. Google will analyze your link based on the topic of the referring page and how thematically consistent it is with yours.
You know that it’s impossible to control where you get links from. Anyone can share your content and link to it however they please.
Since you can’t control your anchor texts or where the links come from, you should use your brand name as anchor text more often.
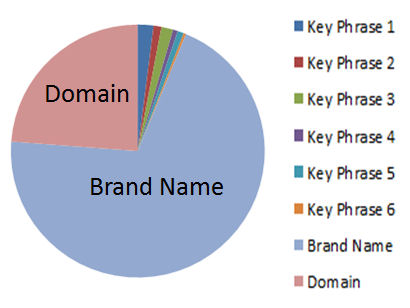
If you’re a social media expert and you’re interviewed by a car blog, you should use your brand name as anchor text.
That’s because these topics — cars & social media — aren’t thematic or closely related and Google uses the anchor text of external links to the page to judge the quality, relevance and usefulness of any link gotten from there.
Last, but not least, make sure that you get links from high-quality sites, disavow low-quality links from thin pages, blend nofollow links into your link profile to make it natural and publish fresh content to increase brand mentions.
5. Relevance : Off Page SEO checklist
Backlinks are effectively votes. If a site links to you, they’re vouching for the quality of your content or business. But not all of these votes are created equal. The relevance of the linking website and web page also matters.
Let me explain why with an analogy.
Say that you’re looking to hire a catering company for your wedding. Two of your friends recommend two different companies. You like both of your friends equally, but one of them is an accountant, and the other is a chef. Who are you going to trust? It’s a no-brainer—the chef.
Things work much the same way online. If you’re a catering company and you have a link from a food blog, then that’s likely going to carry more weight than a link from finance blog.
But, is relevance more important than “authority?”
To try to answer that, we asked a few SEO professionals a simple question:All else being equal, would you rather have a high-authority link with low topical relevance or a low-authority link with high topical relevance?
Here are their answers:
I like relevance better than authority, but I would say that my answer would depend on what the goal is. If it’s to get better rankings quickly, I’d probably go with high-authority/low topical relevance. If sustained rankings/traffic/conversions were my goal, I’d go for lower-authority high topical relevance.

Julie Joyce, Founder Link Fish Media
I go back and forth on this, and I think context matters a lot (i.e., the competitiveness of the space, the authority of the site, etc.). That said, most of the time I’d go with the authoritative link. Particularly in competitive markets, it’s tough to rank without authority (regardless of how relevant my other links are). I can make up for some of the relevance issues by optimizing keywords, internal links, etc.

Paul May, Co-founder Buzzstream
If a client needs to drive some juice into a money page, I have found the larger DR links (even if not super topically relevant) tend to move the rankings more. That said, if traffic is equal and the campaign goal is targeted referral traffic and conversions, then I’d lean towards the lower authority topically relevant link.

Robbie Richards, Founder RobbieRichards.com
I would rather have the link that my competitors will find harder to get.
If the high-authority link with low topical relevance comes from an article in a newspaper or magazine, then I’ll take it. There is an editorial decision being made, so I trust the judgment of the journalist or editor, and I’m confident that the link has been added because they considered that it would offer value to their readers.
That being said, I would not publish irrelevant content on my site in the hopes of attracting high-authority links from media outlets. It might work once or twice but eventually, journalists start asking, ‘why did [brand] release content about [irrelevant topic]?’
In short, low-authority links with high topical relevance will be easier to land, so I pick the high-authority link.

Gisele Navarro, Operations Director NeoMam Studios
How to Get Relevant, Authority and User-Friendly Backlinks
Almost 100 billion searches are made on Google every month for content, products, and services. And that’s just a portion of the market.
This was announced recently at Re/code’s Code/Mobile conference by Amit Singhal, senior vice president of Google Search.

He also explained that more than half of those searches are coming from mobile devices.
To the majority of SEOs, content marketers, and bloggers, backlinks are the most important off-page SEO factor. And, they might be right.
That’s because natural links from authoritative and relevant websites act as an independent “vote of confidence,” that helps search engines trust your website more.
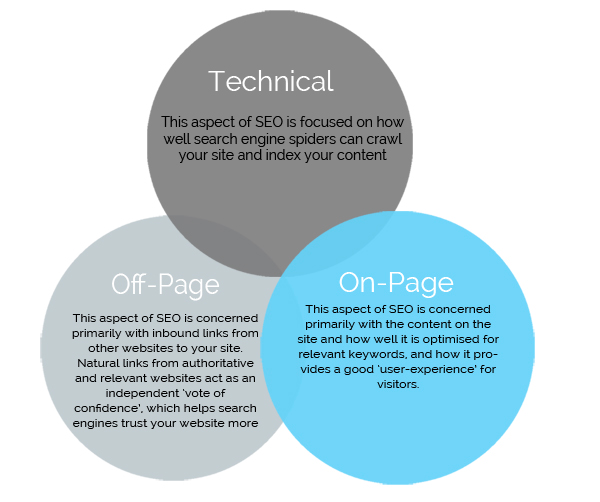
When Google’s search spider crawls your site, looking for fresh content (sometimes depending on your sitemap settings), it indexes your new pages and prepares them for search users.
After your pages are added into its vast index to be returned in search results when relevant search queries are triggered, Google uses several algorithm factors to determine where those pages will rank.
In the SEO world, we refer to these as Google’s ranking factors. They’re the determining factors for organic web page rankings. Fortunately, you don’t have to memorize all of the ranking factors — good news, because according to Google, there are over 200 of them.
But the most important factor as far as SEO is concerned is links. Well, not the links per se, but the impact of such links. Some other off-page factors are:

In the past, if I generated 100 links to my page, and you had only 20 links, Google would view my web page as more authoritative and valuable than yours.
Link quality wasn’t all that important at the time.
But today, links are perceived differently. A lot of questions arise when Google sees a link pointing to your web page. For example:
- Where does the link come from?
- What prompted the site owner to link to you?
- What is the link quality? (I.e., is it from an authority site?)
- How fresh is your link?
- How natural is your link profile?
- And so on…
When building links to your site or internal pages (which is more ideal in today’s SEO), focus on relevant, authority and SEO-friendly links.
Broken link building:
But, guest blogging can only take you far. Worse, it requires a lot of research for the right topic. Then you have to find the right blogs, write the post, submit the post and wait for it to be published.
On the other hand, broken link building is easy, faster than guest blogging and could provide a substantial avenue to earn the right links.
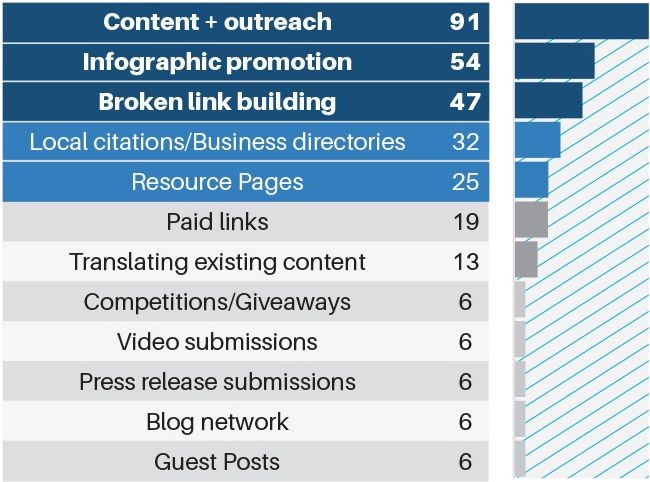
When I launched my nutrition blog, I leveraged broken link building tactics and generated a handful of natural links from trusted sites through that strategy.
The opportunities are just endless when you capitalize on dead links. Because in reality, the internet is broken…literally.
Lots of links that you see on authority blogs are actually dead. As hosting expires, sites are messed up during file transfer or migration or typing mistakes happen and links are bound to break. They lead to 404 error pages, which don’t appeal to users (more on this later).
All these broken links are to your advantage.
There is nothing new or fancy about fixing broken links. This link building tactic will never become outdated or fizzle out, because the internet will always have new broken links that need to be fixed.
If you have too many dead links on your blog, and are wondering whether your search performance will be affected, you don’t have to worry. According to the Official Google Webmaster Central blog, 404 error pages or broken pages won’t affect your site’s ranking.
404s are a perfectly normal part of the web; the Internet is always changing, new content is born, old content dies, and when it dies it (ideally) returns a 404 HTTP response code. Search engines are aware of this; we have 404 errors on our own sites, as you can see above, and we find them all over the web. In fact, we actually prefer that, when you get rid of a page on your site, you make sure that it returns a proper 404 or 410 response code (rather than a “soft 404”).
Although Google likes to see a proper 404 error page, do you think it’s a good experience for the user? Absolutely not.
When people click on your web page from an organic results page, they’re not expecting to see a 404 error page, but rather want to see the exact content they searched for.
Imagine how frustrated people will be when they searched for “best digital wrist watch,” only to click on the first result and see an error page.
A few of these searchers will likely mark the site address and vow never to visit again. Obviously, the user experience was poor. And there’s nothing that drives people away more than a poor user experience, which is a natural indication of your overall customer service to the searcher.
The result of this can be disastrous. According to Sacramento Design Network, “85% of your business could be lost due to poor customer service.”

In a nutshell, broken link building breaks down to four simple steps: conduct a backlink analysis on a relevant website, find a broken link, contact the owner, and let them know about their dead links.

Since you’re helping the site owner locate non-functional links, they might do you the favor of including a link to your website. Ideally, offer a replacement link when appropriate.
If I linked to a particular web page from my Neil Patel blog and found the links to be dead, I could easily replace it with another relevant and high-value resource. If that high-value page belongs to you, that’s both SEO juice and a valuable link.
Trust me, you can get it right the first time, and build the right links to your web pages using this tactic. You’ll find these resources really helpful:
6. Traffic
We studied the top 10 rankings for 44,589 non-branded keywords and found a clear correlation between the top-ranking pages and the sum of organic traffic to their referring pages.
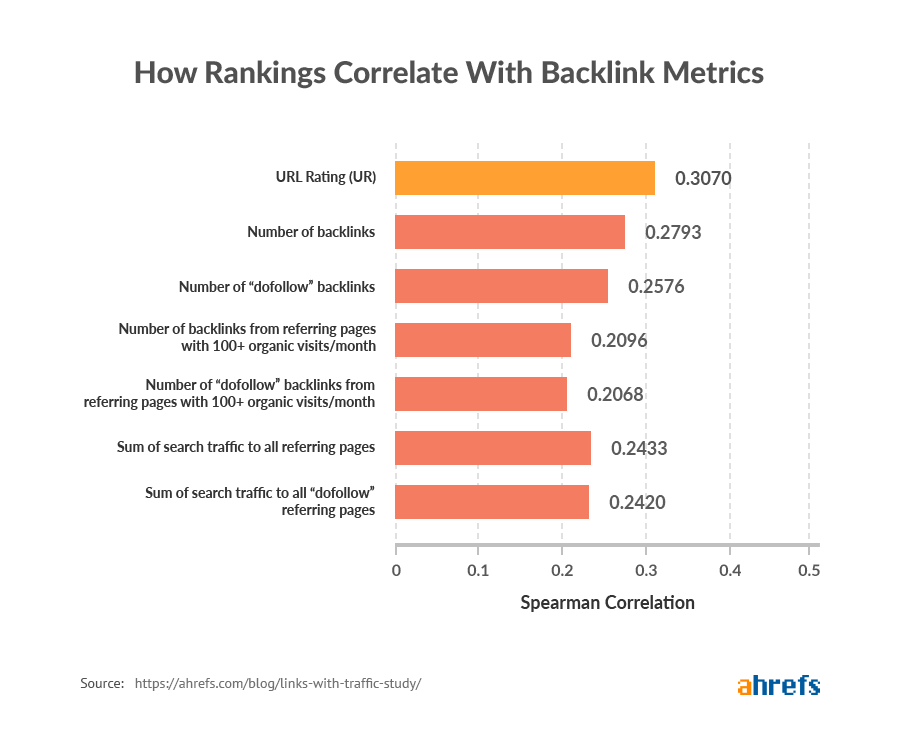
This suggests that links from pages with lots of organic traffic have more weight than links from pages with little or no organic traffic.
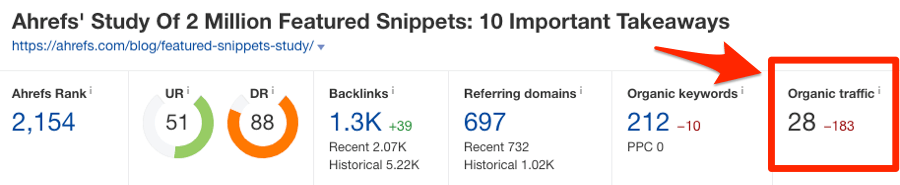
You can see the estimated organic traffic to any webpage in Ahrefs Site Explorer.
You can also see organic traffic to referring pages in the “Backlinks” report.
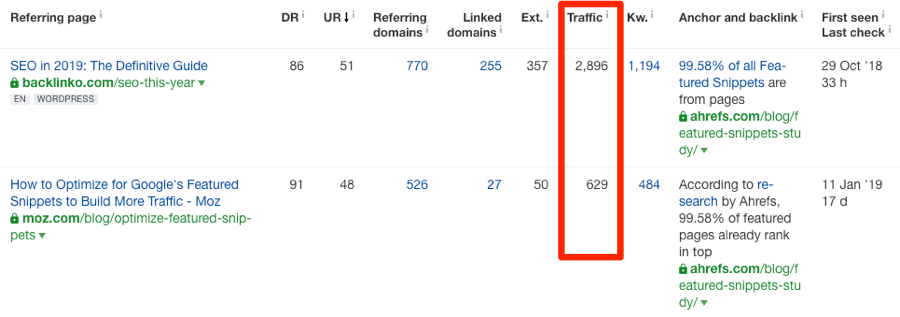
If you’re looking to replicate your competitors’ backlinks, or are pursuing a link building tactic like the Skyscraper Technique, you can quickly sort the report by organic traffic to prioritize and pursue links from the most high-value pages.
Still, while it does make sense to prioritize links from pages with traffic, there’s no evidence to suggest that links from pages with little or no traffic are worthless. If the linking pages are relevant and have some level of “authority,” then you should absolutely still pursue them.WHY LINKS ARE STILL A RANKING FACTOR
Given that PageRank is around two decades old, you might be wondering why links are still such a critical ranking factor in 2019.
The reason is simple: They remain one of the most difficult to manipulate.
While there are some shady ways to acquire backlinks, earning high-quality links is generally quite difficult. People don’t usually link to content unless it’s of some value to their visitors.
Non-link-related off-page factors
Off-page SEO refers to anything done outside of your website with the potential to affect search engine rankings. Building links is the most obvious example of that, but there are many other off-page factors besides links.
If you’re a local business that wants to rank locally, then you should pay particular attention to this section as many of the factors below are specific to local SEO. Those factors are marked with a (*).
1. NAP citations*
NAP citations are online mentions of your business, which also display your business name, address, and phone number—collectively known as NAP (Name, Address, Phone).
According to Moz, citation signals are one of the top local off-page ranking factors.
That means if you’re a local business and want to rank locally—whether in Google’s “snack pack” results or the regular organic search results—then citations are crucial.
You can find many of the citations you already have by Googling something like this:
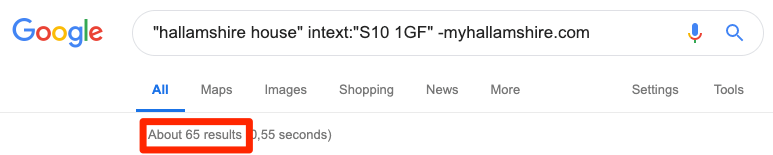
If you do the same for your competitors, then cross-reference the websites that appear in the search results, you can easily find more sites on which to build citations. However, this is a bit of a hassle, and it’s also tricky to judge which citations are likely to move the needle as far as rankings are concerned.
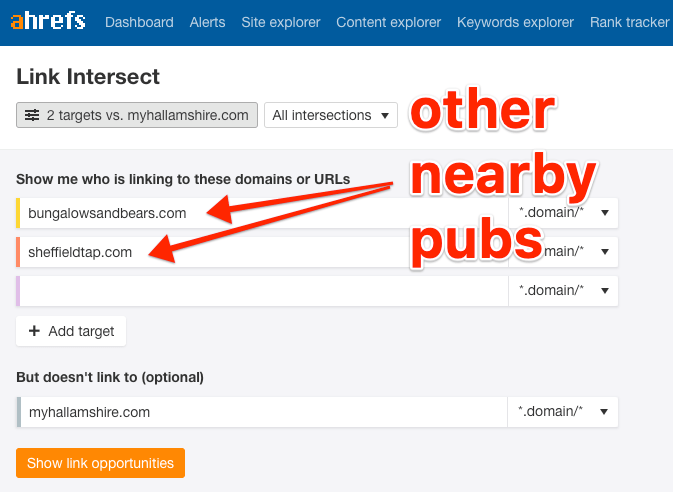
One solution is to use a dedicated tool for finding citations (e.g., Whitespark). Another is to use something like Ahrefs’ Link Intersect tool, which looks for websites that link to multiple competitors, but not you. Because many NAP citations also have links, albeit nofollowed ones, this usually reveals the citations your competitors have, but you don’t.
To use it, paste a few competing websites in the top section, and your site in the bottom part.
Hit the caret to reveal more details about each backlink. Look for ones that appear to be from citations.
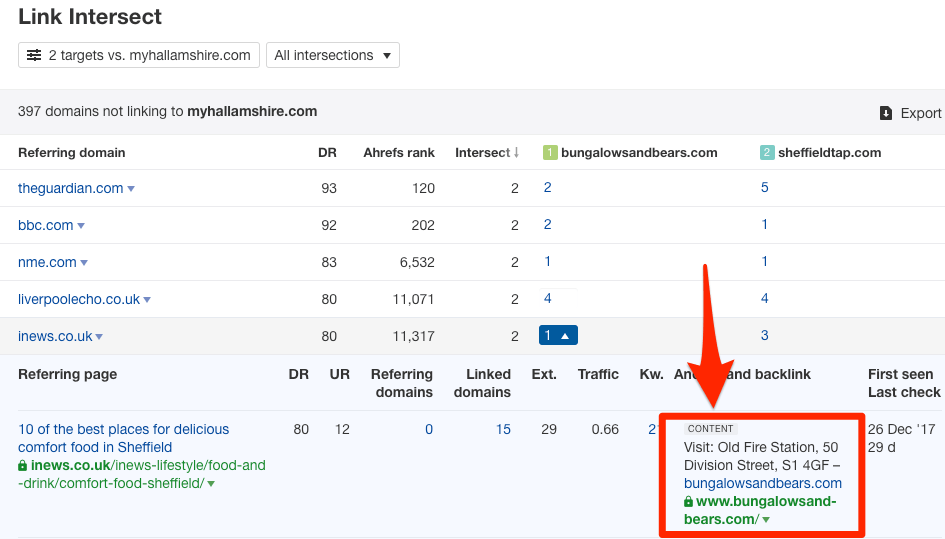
TIP
It’s also important that your NAP information is as consistent as possible between citations, as this allows Google to effectively tie those citations together as part of your online profile.
2. Brand mentions
Brand mentions can be either linked or unlinked.
Linked mentions have SEO value for obvious reasons, but what about unlinked brand mentions?
Google talks indirectly about unlinked brand mentions in one of its patents, which references a system for effectively tallying up express links (linked mentions) and implied links (linkless mentions).
Here’s an excerpt from that patent:An express link, e.g., a hyperlink, is a link that is included in a source resource that a user can follow to navigate to a target resource. An implied link is a reference to a target resource, e.g., a citation to the target resource, which is included in a source resource but is not an express link to the target resource.
Here, Google is effectively saying, “Hey, we know that people often cite brands and content without linking, and we think that such mentions deserve to factoring into our ranking algorithm along with linked mentions.”
Logically, this makes sense. The only real difference between an unlinked and linked mention is that one is clickable and thus may result in more referral traffic.
So, if brand mentions are likely an off-page ranking factor, how do you get more of them?
Here are a few ways:
- Write guest posts
- Be a guest on podcasts
- Do blogger outreach
- Go viral (easier said than done)
You can also use tools like Google Alerts to track new competitor mentions, then jump in on the conversion where appropriate. For example, if you were working for MailChimp, you could set up alerts for new mentions of competitors like ConvertKit and ActiveCampaign.

Setting up an alert in Ahrefs Alerts.LINKED MENTIONS > UNLINKED MENTIONS
Google may indeed be able to assign some value to unlinked mentions, but linked mentions are preferable—even if just for the referral traffic. For that reason, it’s often worth reaching out to all the people who mention your brand without linking and asking them to “make the mention clickable.”
Learn how to do that in our guide to converting unlinked mentions to links.
[amazon box=”B084LF85PC” “small”]
3. Google My Business*
Google My Business (GMB) is a free business profile from Google.
It’s these profiles that rank in Google’s “snack pack” results that you see at the top of the search results for queries with local search intent.
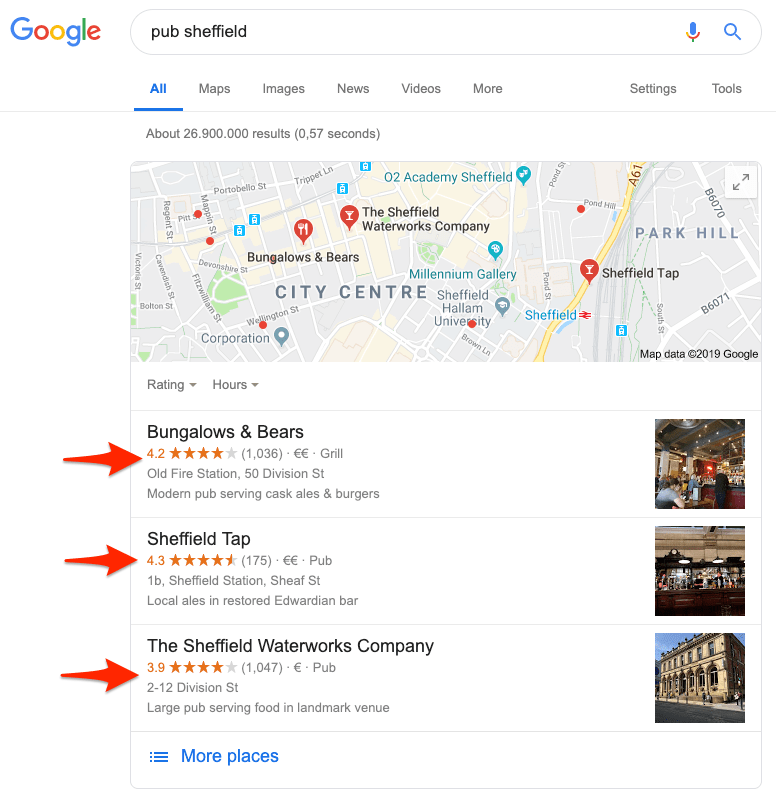
However, merely claiming your GMB profile isn’t enough.
Moz found that an optimized Google My Business profile is the most important ranking factor for ranking in “snack pack” results, and the fourth most important factor for regular local organic search.
Long story short, if you want to rank for queries with local intent (e.g., “plumber near me”), then claiming and optimizing your GMB profile is the most critical component of your off-page SEO efforts.
4. Reviews*
Moz found that review signals are the third most important factor for ranking in Google’s “snack pack” results, and the fifth most important factor for ranking in regular local organic search.
Generally speaking, the more positive and genuine reviews you have on your Google My Business profile and on trusted third-party sites, the higher you’re likely to rank in the “snack pack.” Negative reviews have the opposite effect.
The same study also found the “authority of third-party sites on which reviews are present” to influence regular local organic rankings.
5. Social signals
Google’s official stance is that social signals are not a direct ranking factor.
But some people don’t believe this, probably because of outdated studies like this one that show a correlation between rankings and social shares.
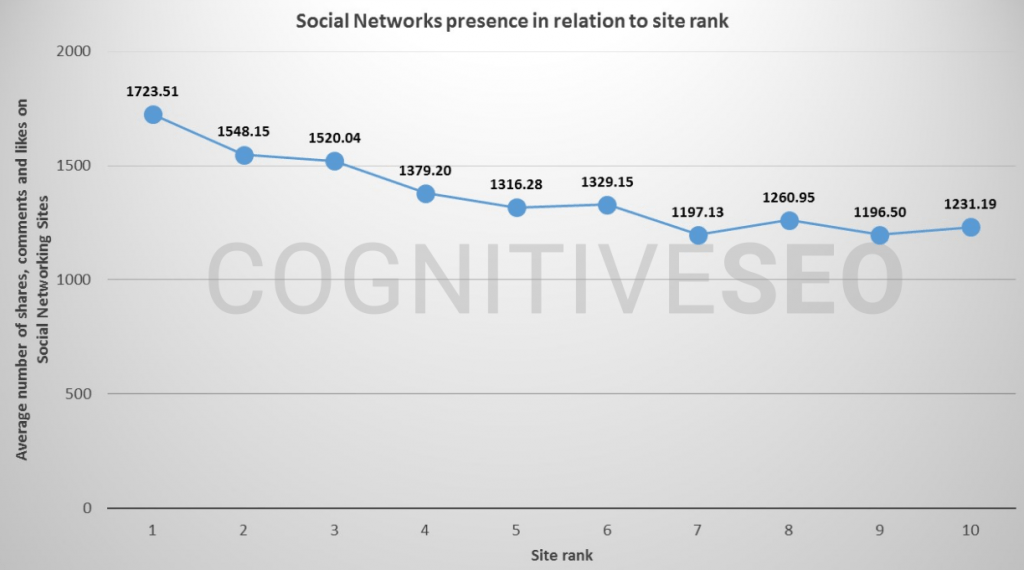
So, who is correct? Our verdict: Probably Google.
The main reason is that it’s easy to manipulate social signals. You can buy thousands of social shares for a few dollars on sites like Fiverr. Generally speaking, things that are this easy to manipulate don’t make for reliable ranking factors.
Having said that, there’s no doubt that genuine social shares do have a positive influence on rankings—albeit an indirect one. Why? Because real social shares lead to more eyeballs on your content, and more eyeballs lead to more links, mentions, and all those other off-page SEO factors that we know to have a direct effect on rankings.
Create and distribute compelling infographics: There’s no doubt about it – infographics still work and will likely continue to work in the future.
While infographics can still yield impressive results, you have to understand that not all infographics will get the job done.
If you were reading QuickSprout in Q1 and Q2 of 2015, you’ll most likely agree that my infographics are top notch. In fact, I spend up to $1,000 to have a single infographic designed.
However, if you’re on a tight budget or just starting out, you may not be able to afford $1000 infographics.
Alternatively, you can use Dribbble to find professional infographic designers for half the price. If you decide to use Visual.ly, you’ll get a better design – but their service costs more.
A lot of content marketers still use infographics to attract the right audience, acquire authority links, and grow their email list.
For instance, Ken Lyons shared a case study recently of how WordStream created a useful infographic that helped a lot of people. Interestingly, the infographic earned a link from CNN, and drove loads of traffic to its site.
Ann Smarty, a prolific content marketer, created a useful infographic that generated 10 powerful links in just 2 days.
Right Casino Media also generated more than 10 quality links from strong domains with its infographics.

Whether you’re a B2B or B2C company, you can use visual marketing to drive engagement with your target audience and earn editorial links from the right sites.
What’s more, your ideal customers will respond better to visual content than plain text. Data from HubSpot found that the human brain processes visual information 60,000x faster than plain text.
That might help explain the continuing demand for infographics, which has increased by 800%.
Here’s the current growth trend:
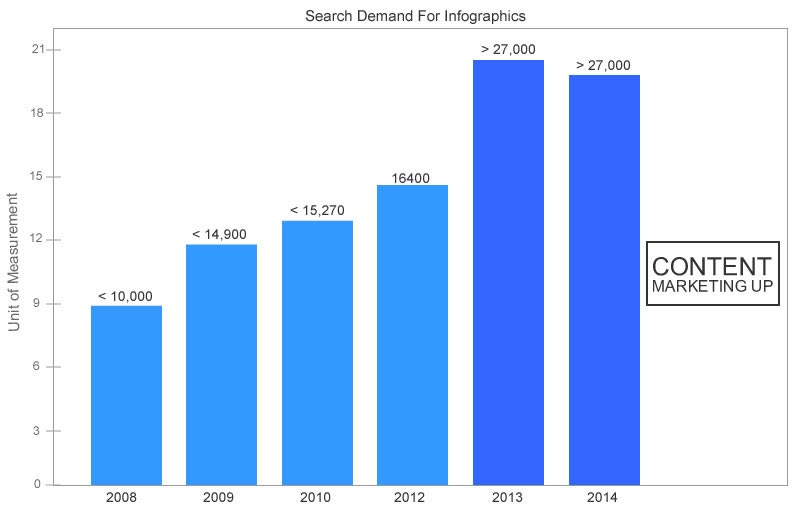
I love creating and distributing compelling infographics. Like any compelling content, when you give it sufficient initial promotion, an infographic has a greater chance of going viral.
How to Avoid Google Penalties for Unnatural Links
Backlinks are really important, especially if you want to sustain your site’s ranking position. But we can’t talk about off-page SEO without mentioning Google penalties and unnatural links.
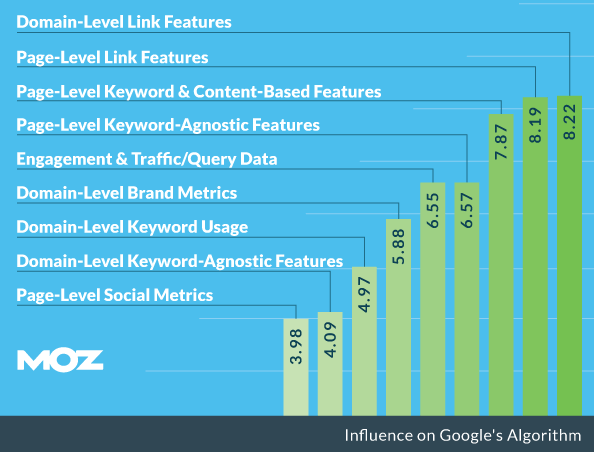
The truth is that links can significantly affect search performance – for better or worse.
If you ask pro bloggers which factor they think has the strongest impact on search rankings, many of them will say “links.”
Top brands, small businesses and blog owners are also into link building. Data from MarketingSherpa’s 2012 Search Marketing Benchmark Report found that 59% of companies have done external link building.
You want to avoid Google’s penalty as much as possible, because recovering from a penalty can be daunting and very difficult.
Many things that used to interest Google — such as links from high PR sites — no longer have that strong impact.
Google is now more concerned about user optimization, user intent and valuable content. The focus is no longer on the search phrases people use, but their purpose for using that particular phrase.
A full backlink analysis can help you pinpoint which links are good or bad for your site – and how to stay off Google’s penalty radar.
The search engine giant hasn’t yet clued the SEO community into any step-by-step process for staying safe. However, there are things you can do to ensure that your site isn’t penalized.
These best practices have helped me generate over 700,000 blog visitors to QuickSprout without experiencing any penalty due to unnatural links and over-optimized anchor text.
i). Create content and optimize for the users first: You probably already know what this means. The question is, are you putting your users first?
To truly put users first, forget about mentioning your keywords several times in the post, especially if it doesn’t flow naturally.
Putting users first goes beyond keyword usage. Sometimes you may not outright target any keyword, yet somehow your content looks too promotional.
Users don’t like to be sold. Instead, help them by creating valuable content. As much as you can, integrate data into your blog posts, and use visuals to convey your message clearer.
If you help them with great content, they’ll want to know more about you.
Final thoughts
Off-page SEO might seem harder than on-page SEO because many off-page factors aren’t entirely under your control, but that’s the whole point. The harder something is to earn, the more reliable it is as a ranking factor.
It’s also important to note that traditional online and offline marketing activities can indirectly influence many of the factors above.
For example, when Tesla launched a car into space in 2018, there was a considerable spike in the number of published articles online mentioning Tesla.
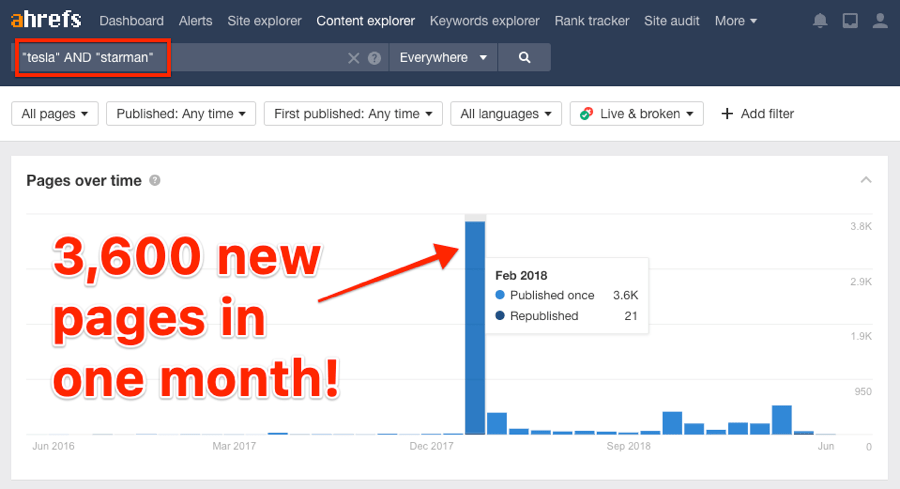
Many of these sites also linked to tesla.com from their articles.
While launching a car into space is unlikely to be a viable marketing stunt for most businesses, it doesn’t have to be. Chances are you don’t need thousands of links or brand mentions to rank, so smaller scale offline marketing activities work well for smaller businesses.
[amazon box=”B084LF85PC” “small”]