World Geography : Classification and Importance of Lakes. ( UPSC )
Those stagnant parts of water which are surrounded by land blocks on all sides.
Classification of lakes
(A) On the basis of Salinity
1. Freshwater Lake
- Theses are fresh-water lakes fed by rivers and with out-flowing streams.
- e.g. Great Lakes of North America.
2. Saltwater Lake
- Salt lakes (also called saline lakes) can form where there is no natural outlet or where the water evaporates rapidly and the drainage surface of the water table has a higher-than-normal salt content.
- e.g. Great Salt Lake, the Aral Sea and the Dead Sea.
- Alkali lake- sodium and potassium carbonate.
- Bitter lake- sodium sulfate.
- Borax Lake
- Mixed lake many types of salt are found in it.
(B) Classification on the basis of origin
1. Glacial Lake
- Small basins are formed in the valley by glacial erosion.
- When the snow melts, the water collected in these basins takes the form of a lake, called tarn.
- The lake is called lake garden when it is found in thousands at once.
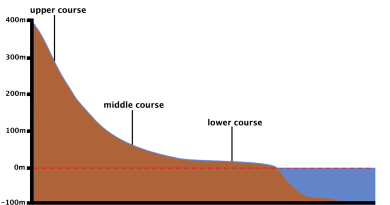
2. Riverized Lake
- Lakes formed by erosion
- Rivers form plungepool Lake (through expansion of plunges)) and Oxbow Lake (by flooding of abandoned river meander) through erosion.
- Lakes formed by deposition
- Alluvial fan lake by deposition (when rivers are blocked by alluvial fans), delta lake (by delta blocking sea water in the Ganges delta called bil ) and lake of flood plain by alluvial soil.
3. Volcanic Lake
- Crater lake
- In dormant or extinct volcanoes, rain falls straight into the crater or caldera which has no superficial outlet and forms a crater or caldera lake.
- Examples: Lonar in Maharashtra and Krakatao in Indonesia.
- Lava blocked lake
- Due to the accumulation of lava in the river valley during the eruption of the volcano, the river water flows down to form a lake.
Diastrophic Lake
- Synclinal lake
- By filling water in the synclines made by horizontal movement.
- Anticlinal lake
- Due to the emergence of the land block in the transverse direction in the river course, the river water is blocked and the uplifted lake is formed.
Fault and rift lake
- A rift valley is formed when two blocks of earth move apart.
- It’s a sunken land between two parallel faults
- Example – East African Rift Valley includes such lakes as Lakes Tanganyika, Malawi, Rudolf, Edward, Albert.
Relict lake
- Remnants of giant lakes that were once filled with glacial meltwater but now exist as separate bodies of water.
Earthquake lake
- Lake formed due to earthquakes.
Lakes due to landslides
- A landslide dam or barrier lake is a natural damming of a river by some kind of landslides, such as debris flows and rock avalanches.
Man made lakes
- man has now created artificial lakes by erecting a concrete dam across a river valley so that the river water can be kept back to form reservoirs.
- Example: Lake Mead above the Hoover Dam on the Colorado River, U.S.A.
Importance of lakes
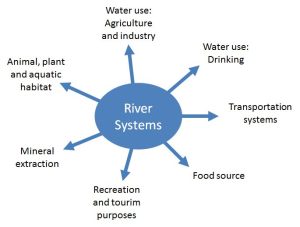
1- Means of communication
- Large lakes like the Great Lakes of North America provide a cheap and convenient form of transport for heavy and bulky goods such as coal, iron, machinery, grains and timber.
- The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence waterways penetrate more than 1,700 miles into the interior.
- They are thus used as the chief arteries of commerce.
2- Economic and industrial development
- The Great Lakes-St. Lawrence waterways were responsible for the development of the interior wheat farms and lakeside industries.
3- Water storage
- Example: Kolleru lake in Andhra Pradesh.
4- Hydro-electric power generation
- Artificial lakes like Hirakud
5- Agricultural purposes
- Many dams are built across artificial lakes.
- Bhakra Nangal Dam. Its reservoir, known as the “Gobind Sagar Lake” and Hirakud Dam (Odisha) on the Mahanadi
6- Regulation of river flow
- Hoover Dam on the River Colorado and the Bhakra and Nangal Dams on the Sutlej in India.
- The Hirakud dam was originally conceived as a flood control measure.
7- Source of food
- Many large lakes have important supplies of protein food in the form of freshwater fish. Sturgeon is commercially caught in the Caspian Sea, salmon and sea trout in the Great Lakes.
8- Source of animals
- Salt lakes provide valuable rock salts. In the Dead Sea, the highly saline water is being evaporated and produces common salt. Borax is mined in the salt lakes of the Mojave Desert.
9- Tourist attraction
- Lake Chilka, Leh, Dead Sea.