World Geography : Classification of Mountains. ( UPSC )
- A hill with a steep slope is called a mountain whose height is at least 900 meters.
Classification of mountains on the basis of height 1. Low Mountains
- Their height has decreased due to denudation
- Height ranges between 500 to 1000 meters
- Ex- Vindhyachal mountain
2. Rough mountain
- Height ranges between 1000 to 1500
3. Rugged Mountains
- 1500 to 2000 meters
- Ex- Appalachian, Aravalli and Western Ghats
4. High Mountains
- More than 2000 meters high
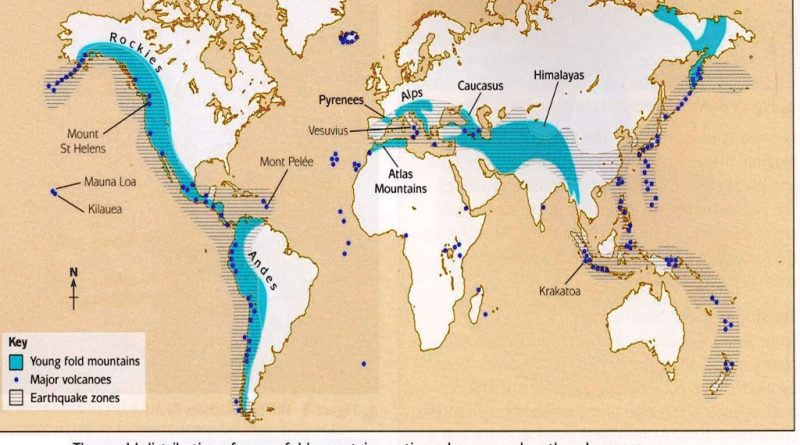
- Rockies, Andes and Himalayas

B. Classification of mountains on the basis of location
- Continental mountains
- Oceanic mountains
1- Continental mountains a- Coastal mountains
b- Inland mountains
- Coastal Mountains
- Located in the Coastal areas of continents
- The Rockies on the western edge of North America and the Appalachians on the eastern edge
- Andes mountains on the western edge of South America
- Alpine mountains on the southern edge of Europe
- Atlas mountains on the northern edge of Africa
- Eastern and Western Ghats on both sides of peninsular India
- Coastal Mountains
- Located in the Coastal areas of continents
- The Rockies on the western edge of North America and the Appalachians on the eastern edge
- Andes mountains on the western edge of South America
- Alpine mountains on the southern edge of Europe
- Atlas mountains on the northern edge of Africa
- Eastern and Western Ghats on both sides of peninsular India
b- Inland Mountains
- Located in the interior of the site away from the coast
- Created by internal land elevations
- The Vosges and the Black Forest (Europe),
- The Kunlun, Tienshan, Altai mountains of Asia,
- The Urals of Russia, the Aravallis,
- The Himalayas, the Satpura, and the Maikal of India.
- Oceanic mountains
- Oceanic mountains are found on continental shelves and ocean floors.
- Mauna Kea Volcano
c. Classification on the basis of mode of origin
- Fold Mountain
- Resulting from the convergence of Plates
- considered as the “true mountains
- Himalaya, Alpine, Rockies, Andes, Atlas
On the basis of nature of folds a- Simple fold mountains
- Simple fold mountains with open folds in which well-developed systems of synclines and anticlines are found, and folds are of wavy patterns.
b- Complex fold mountains
- Complex fold mountains in which the rock strata are intensely
compressed to produce
a complex structure of folds.
- In the Himalayas, over folds and recumbent folds are often found detached from their roots and carried a few hundred kilometres away by the tectonic forces. These detached folds are called

2. Block Mountain
- Created because of faulting on a large scale (when large areas or blocks of earth are broken and displaced vertically or horizontally).
- The uplifted blocks are termed as horsts, and the lowered blocks are called graben.
- Vindhya and Satpura
- Germany’s Black Forest
- Vosges of France
- California’s Sierra Nawada is the world’s largest block mountain
3. Volcano Mountains
- Formed due to the accumulation of lava, fissile material, etc., obtained from the eruption of a volcano, so these are also called mountains of accumulation
- Cotopaxi is the highest volcanic mountain in the world
- They are common in the Circum-Pacific belt.
1. Residual / Relict Mountains
- Remnants of old mountains derived as a result of denudation
- Aravalli, Eastern Ghats, Parasnath Hill
d. Classification of Mountains on the basis of period of origin
1.
Precambrian
- They belong to the Pre-Cambrian period, a period that extended for more than 4 billion years.
- The rocks have been subjected to upheaval, denudation and metamorphosis.
- So, the remnants appear as residual mountains.
- Some of the examples are Laurentian mountains, Algoman mountains etc.
2- Caledonian Mountains
- They originated due to the great
mountain-building movements and associated tectonic movements of the late Silurian
and early Devonian
periods (approximately 430 million years and 380 million years ago).
- Examples are the Appalachians, Aravallis, Satpura ,Scandinavian
3- Hercynian mountains
- These mountains originated
during the upper Carboniferous to Permian Period in Europe
(approximately 340 million
years and 225 million years ago).
- Examples Vosges and the Black Forest, Altai, Tien Shan mountains of Asia, Ural Mountains etc.
4- Alpine Mountains
- Latest Fold Mountains
Examples
- The Rockies of North America, the Alpine mountains of Europe,
- The Atlas Mountains of north-western Africa,
- The Himalayas of the Indian subcontinent
- The mountains radiating from Pamir knot like Pontic, Taurus, Elburz, Zagros and Kunlun etc.
Has its origin in the Tertiary Period (65 million years to 7 million years ago).
GEOSYNCLINE THEORY BY KOBER
- Geosynclines are the area of long, wide, and shallow depression of the water body bordered by rigid masses and get huge sedimentation deposition from surrounding areas.
- Kober explained the concept of geosynclines and mountain building based on the force of Contraction which is produced by the cooling of the earth
- As per Kober, there are two zones:
- Orogen/ Geosyncline-the place of mountain building
- Kartogen / Foreland- Orogen is surrounded by Kartogen.
- As per Kober, there are three stages involved in mountain building: a- Lithogenesis
- Orogenesis
- Gliptogenesis
Lithogenesis
- In this stage, geosynclines are created due to the cooling and contraction of the earth and deposition started.
Orogenesis
- In this stage, the mountain-building process started.
- Over time, due to huge sedimentation deposition in the orogen zone from Kartagen led to an increase in pressure and weight.
Gliptogenesis
- This stage, it involved the gradual increase of the mountain ranges.
- Later, weathering, erosion, and deposition started over the mountains to make further landforms
Criticism
- Force of contraction by cooling is not such power to make high mountains.