On page SEO : Everything you need to know
Succeeding in organic search today requires optimizing for a combination of factors that search engines consider important – technical, on-page and off-page.
Over the years, we’ve seen increased focus toward off-page techniques – such as link building – and other technical elements.
But the reality is, off-page SEO won’t do much good if you don’t pay attention to the fundamentals – on-page SEO.
Smart SEO practitioners know that on-page optimization should be constantly prioritized.
And because the search landscape is ever-evolving, it’s important to make sure your on-page SEO knowledge is up to date.
In this post, we will cover what on-page SEO is, why it matters, and 10 of the most important on-page SEO considerations today.
What Is On-Page SEO?
On-page SEO (also known as on-site SEO) refers to the practice of optimizing web pages to improve a website’s search engine rankings and earn organic traffic.
In addition to publishing relevant, high-quality content, on-page SEO includes optimizing your headlines, HTML tags (title, meta, and header), and images. It also means making sure your website has a high level of expertise, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
It takes into account various aspects of the webpage that, when added together, will improve your website’s visibility in the search results.
Also read : Seo top keyword reasearch tools And Long tail keywords complete guide
Why On-Page SEO Is Important
On-page SEO is important because it helps search engines understand your website and its content, as well as identify whether it is relevant to a searcher’s query.
As search engines become more sophisticated, there is a greater focus toward relevance and semantics in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Google, with its plethora of complex algorithms, is now much better at:
- Understanding what users are actually searching for when they type a query.
- Delivering search results that meet user intent (informational, shopping, navigational).
Adapting to this development is essential, and you can do it by ensuring that your website and its content – both what is visible to users on your webpages (i.e., text, images, video, or audio) and elements that are only visible to search engines (i.e., HTML tags, structured data) – are well-optimized according to the latest best practices.
Additionally, you can’t simply ignore on-page SEO because you have more control when optimizing for on-site elements – as opposed to off-page SEO that consists of external signals (i.e., backlinks).
If you put effort into on-page strategies, you’ll see a boost in traffic and a rise in your search presence.
This guide will walk you through the most important elements of on-page SEO.
Paying close attention to these 10 areas will help improve your content and authority – and increase your rankings, traffic, and conversions.
[amazon box=”B084LF85PC” “small”]
1. E-A-T
E-A-T, which stands for Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness, is the framework that Google raters use to assess content creators, webpages, and websites as a whole.
Google has always put a premium on high-quality content. It wants to make sure that sites producing high-quality content are rewarded with better rankings and sites that create low-quality content get less visibility.
There is a clear relationship between what Google considers high-quality content and what appears in the search results.
Call it correlation or causation – whatever it is, E-A-T is somehow playing a role in Google’s organic search results. Which means E-A-T must be a consideration in your SEO strategy.
Essential Tag Fundamentals
Do you take meta tags seriously? Although the effect of the title tag or meta description has changed significantly over the past several years, it’s still a good practice to pay attention to them.
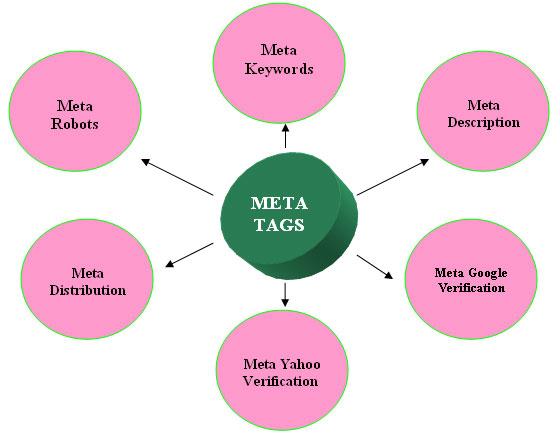
In on-page SEO, the major types of meta tags that you should pay attention to are:
Title tags: Title tags define the title of your web page or document. They’re mostly used to display preview snippets of your web pages. When you’re writing your title tag, it should be short, clear and descriptive but don’t duplicate content from the page content.
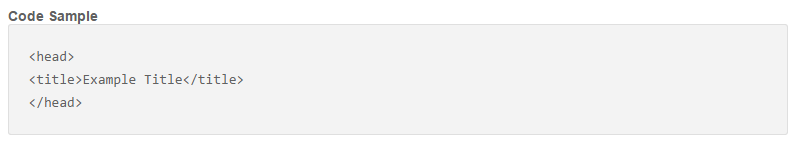
The ideal length is 50 – 60 characters. If your title tag exceeds 60 characters, Google will only show the first 60.
You can use Moz’s preview tool to preview how your title tags will appear in the search engine.
Meta description:
This is how a meta description usually appears in the organic search listings:
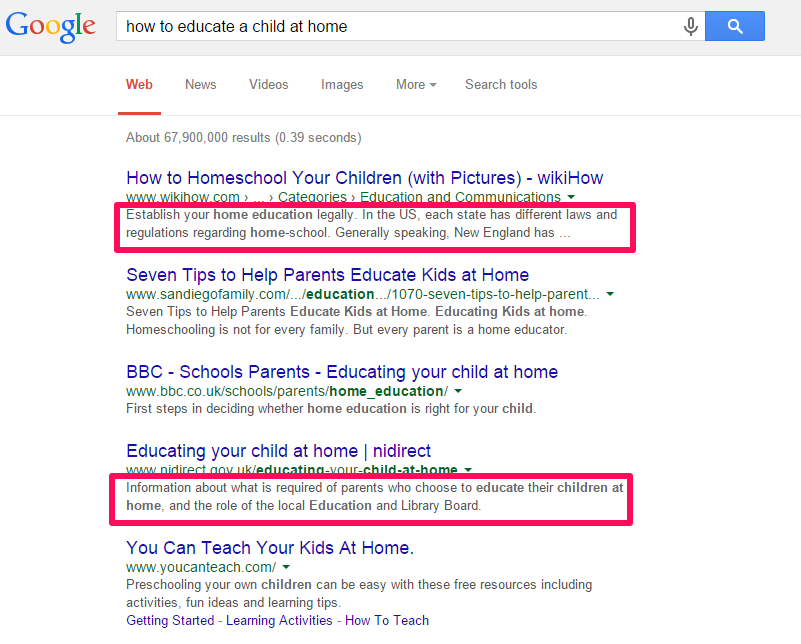
The meta description is what search engines use to gauge what topic you’re writing about and the exact audience that they should send to that page. So, make it descriptive and short – no more than 160 characters.
There is no need to stuff keywords in your meta description (which would work against you anyway). 160 characters is just not enough space for stuffing. Instead, use synonyms or latent semantic indexing (LSI) of your main keyword to get on-page SEO in the meta description, keeping search engines happy.
For example, if your main keywords in the headline are “generate website traffic,” here are LSI keywords that you can use:
- get site visitors
- drive free traffic
- attract site visitors
- attract website visitors
You can often find other related keywords beneath your search engine results. Those are also variations that you can use in your description:
2. Title Tag
The title tag, an HTML tag that exists in the head section of each webpage, provides an initial cue or context as to what the topical subject matter is of the respective page it is on.
It is featured prominently in the search engine results pages (typically used as the clickable link) as well as in the browser window.
The title tag by itself has little impact on organic rankings, this why it’s sometimes overlooked.
That said, missing, duplicate, and poorly written title tags can all negatively impact your SEO results, so make sure you’re optimizing for this element.
3. Meta Description
Since the early days of SEO, meta descriptions have been an important optimization point.
Meta descriptions, meta tags that provide a description of what the page is about, are often displayed in the SERPs underneath the title of the page.
While Google maintains that meta descriptions don’t help with rankings, there is anecdotal evidence that indirect attributes of better descriptions do help.
Optimizing meta description correctly can help improve:
How has the competitive landscape changed?
Find out if your competitors secured their market positions in recent months
- Click-through rate (CTR).
- Perception of the quality of the result.
- Perception of what your website offers all change.
4. Headlines
Want your website content to perform well on search? Then start writing compelling headlines.
Coming up with a title for a blog post might seem too basic, but a great headline can mean the difference between a click and an impression – that’s why it’s important to create them strategically.
Your headlines need to spark interest for it to stand out on the SERPs – enticing users to click through and continue reading the rest of the content.
5. Header Tags
Header tags are HTML elements (H1-H6) used to identify headings and subheadings within your content from other types of text (e.g., paragraph text).
Header tags aren’t as critically important for your site rankings as they used to be, but these tags still serve an important function – for your users and your SEO.
They can indirectly impact your rankings by:
- Making your content easier and more enjoyable for visitors to read.
- Providing keyword-rich context about your content for the search engines.
6. SEO Writing
SEO writing means writing content with both search engines and users in mind.
There is a strategy behind writing solid SEO content – and it is more than just keyword research and fill in the blanks.
Simply producing content for the sake of it won’t do. Remember that you’re writing content for people – therefore that content must be high-quality, substantial, and relevant.
[amazon box=”B084LF85PC” “small”]
7. Keyword Cannibalization
True or false? The more pages you have targeting a keyword, the better you’ll rank for that keyword.
False!
Targeting a specific term across multiple pages can cause “keyword cannibalization” which has some potentially disastrous consequences for your SEO.
When you have multiple pages ranking for the same keyword, you’re actually competing with yourself.
It’s important to identify whether keyword cannibalization exists on your website and resolve it right away.
8. Content Audit
Most content creators are focused on creating new content that they forget to audit their existing content. And this is a mistake.
Auditing your existing content is crucial because it helps you:
- Evaluate whether your existing content is achieving its goals and gaining ROI.
- Identify whether the information in your content is still accurate or has become stale (or even outdated).
- Determine what types of content are working for you.
Content audits can greatly help your SEO strategy and they should be done on a regular basis.
9. Image Optimization
Adding images is a good way to make your webpages more appealing. But not all images are created equal – some can even slow down your website.
Optimizing images properly will help you make the most of a valuable SEO asset.
Image optimization has many advantages, such as:
- Additional ranking opportunities (show up on Google Image Search).
- Better user experience.
- Faster page load times.
Images shouldn’t be an afterthought. Make sure to incorporate images that support your content and use descriptive titles and alt text.
10. User Engagement
Enhancing your website’s on-page SEO elements is only half the battle.
The other half lies in making sure that users will not bounce – but instead, they’ll continue viewing your content, interacting with it, and keep coming back for more.
Retaining engaged users is a great challenge in itself, but it’s certainly doable. To increase user engagement, focus on aspects such as site speed, user experience, and content optimization, among others.
3. Creating Content That Drives Search Traffic
Content is the backbone of a thriving business and on page SEO is the backbone of content marketing. You’ve probably heard the saying, “content is king.” But, there is way more to successful content marketing than just “content.” You have to publish the kind of content that will drive traffic and grow your business.
This involves using specific keyword phrase components that include long-tail anchor words.
You’ll also notice that when you start creating in-depth content, you’ll see a corresponding increase in traffic from long-tail searches, a very specific keyword phrase indicating buyer positioning and urgency. These help search engines give you juice because you are helping people solve problems with your content.
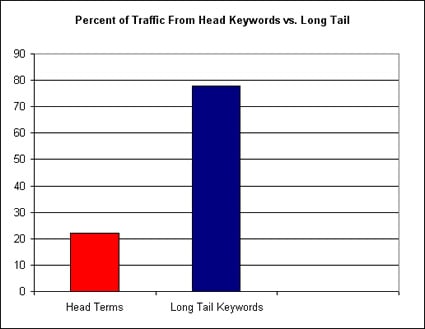
These days, your customers are smarter than you think. You have to be willing to listen to and learn from them – their search for solutions motivates them to ask certain questions. Those questions can tell you exactly what they want most from you.
Content that drives traffic …
Is practical, useful and valuable
- Is interesting to read
- Is in-depth and well-written
- Is written with the user in mind
- Solves a problem
- Is easy to share
- Is optimized for a high-volume keyword
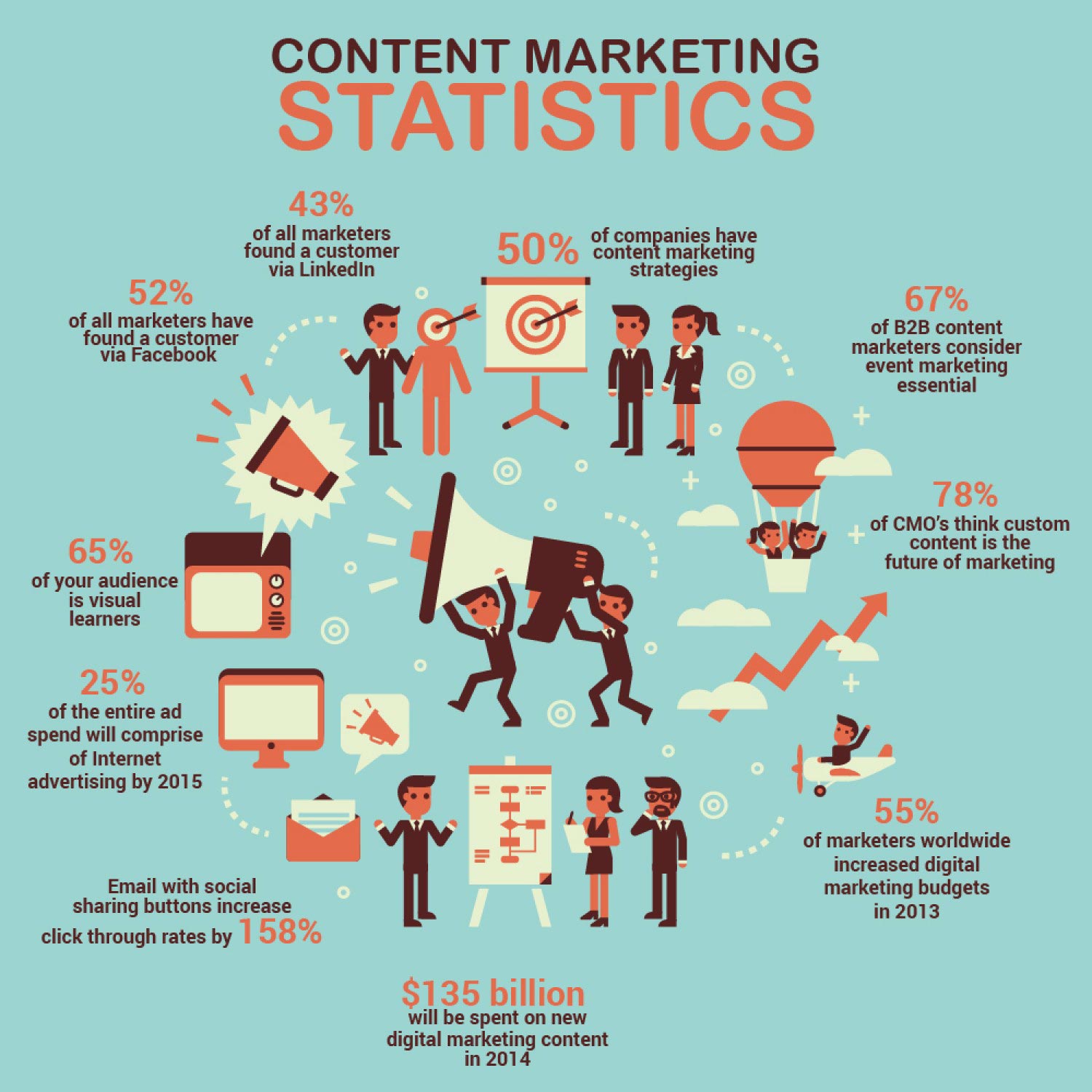
According to Demand Metric, 76% of online shoppers felt excited and closer to a company after reading its custom content. That’s why 78% of CMOs consider custom content to be the future of digital marketing.
Duplicate content was once an easy cheat to getting content so search engines would see more stuff, but duplicate content is now easily found by search algorithms and penalizes the culprit.
Traffic-generating content makes the user happy. So, we’re going to start with the aspect of content marketing that matters most: user experience optimization.
It often starts with a keyword phrase relating to what the user is searching for.
An overview of user experience optimization: On-page SEO begins and ends with the user. No one should build a site for search engines. We build sites for people. After all, search spiders won’t write a comment, subscribe to your list or buy your product. Only your users can do that.
On-page SEO consists of those activities that directly affect the content, pages, and architecture of the site – in other words, all of the internal factors that make a site useful for the visitor.
User optimization is all about presenting your content and design so that users can find what they’re looking for immediately – another reason that you need to speed up your site load time.
As part of the user experience, you may have duplicate content in your site map. This may be important for consumer ease of use, but make sure to let the spiders know not to index for the duplicate content to improve search engine speed.

It’s all about creating positive experiences for your users. One study, by Ruby Newell-Legner, concluded that it takes 12 positive experiences to make up for one unresolved customer experience.

User optimization is all about answering search users’ questions with easy to read content, not merely targeting their keywords. For example, if customers are searching for “electric guitar lessons,” here is the wrong way to write your headline and introduction:
Easy Electric Guitar Lessons For Those Looking To Learn Electric Guitar
Do you want easy electric guitar lessons that will make you play guitar like a hero? Well, this electric guitar lessons post will definitely guide you on the right path, so you can master the electric guitar chords in 30 days or less.
The above headline and introduction are not optimized for the user. The keywords are stuffed and the article introduction is confusing, if not at least lame.
To help you understand what user optimization is about, let’s write a better headline and introduction, while still targeting the keyword “electric guitar lessons:”
Best Electric Guitar Lessons That Will Turn You Into a Pro
What is the best way to learn guitar at home? Many people prefer to read books, but there is a better way. Take some electric guitar lessons from a professional who knows what he’s doing. I don’t want to flaunt my guitar skills here, but trust me, I can help you master the art.
See the difference? In the second example, the main keyword phrase appears once in the headline and just once in the introduction. Moreover, the opening doesn’t promise anything that sounds too good to be true. The reader will understand the second article better because it was optimized for them.
Remember that when it comes to user experience, use of keywords is not the major factor. Instead, the critical issue is addressing the user’s intent – in other words, the reason why the user is searching for that particular keyword.
When you do your on-page search optimization efficiently, your listing will be more attractive and the users will benefit, as a consequence, even before they click to visit your web page.
Brian Clark put it well, when he said that Google is like an infant who doesn’t know what to do and relies on you as a guide.
In his words, “you’ve got to spoon-feed search engine spiders with valuable content that the users will be excited about.”
And, over the years, Clark and his prolific team have produced some of the best blog posts and articles around. Through consistent and proper use of keyword phrase content marketing techniques, Brian Clark turned a blog (copyblogger.com) into a $7 million digital company.
Another important aspect of user experience is functional design. Steve Jobs knew that design isn’t just “how a device looks” but also about “how it works.”

Other great things that make the social site a good fit for the user are:
Another example is the Apple brand juggernaut. Many companies focus on selling features, but Apple also believes in the power of good design.
Apple customers trust the brand completely and happily recommend it to others, not because it’s the most affordable or sophisticated, but because of the sleek design and how the Apple experience makes their lives better.
Another site that thrives on good user experience, is easy to navigate, is legible and has a nice choice of colors combined with high-quality content is HubSpot.com.
Understand the Google Panda algorithm: The Panda algorithm update was first released in February 2011. It was designed to help Google return high-quality results when users type a keyword phrase into the search box.

While other updates have come and gone, Panda’s effect is still going strong. You may recall that Panda penalized low-quality content and thin sites. If you consider the state of search now, you’ll agree with me that Google’s ranked top results have vastly improved, since Panda.
Marketers have come to realize that nothing spectacular can be achieved without the right content.
Panda made it easier for smart content marketers to start creating a conversation with their content. You give insights and advice to your customers and they respond with their questions, appreciation or suggestions.
That’s the reason for Google Hummingbird, as well – to bring the user and the marketer together and meet the user’s needs.
If you want to improve your search rankings, you need to consider two aspects of your content:
Avoid low-quality content: The days of generic content with no value are long gone. Enough said.
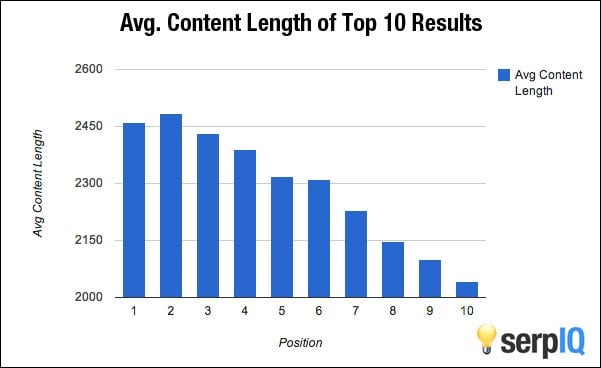
Avoid thin content: Your content may be high-quality, in terms of the information that you share, but if you want to give your blog a boost in the SERPs, you’ve also got to increase your content length.
No more 300- or 500-word posts, unless you’re also using an infographic on the same page. Instead, write in-depth articles of 2000 words or more, because recent content length affects rankings.
98% of the articles that I publish on this blog contain around 5,000 words. And, by being consistent with the creation of in-depth content that offers a lot of value, I’ve significantly improved my search rankings for several keywords. It also helps link building because there are simply more areas to redirect to. For example, I rank #3 for a highly targeted keyword, “blog traffic.” See for yourself:
Content freshness: The percentage of content, within a page, that remains fresh, has an effect on the site’s rankings. Google takes freshness very seriously.
As a result of this, Google now prefers fresh content, breaking news and other recent content updates that deal with trends.
When it comes to on-page SEO, you may be wondering how Google scores fresh content. Well, according to Amit Singhal, “different searches have different freshness needs.”

Freshness as a ranking factor isn’t new. Over the years, even before the Document Scoring Based on Document Content Update, which Google’s engineers filed a patent for in 2003, the Google search engine had scored content based on freshness for many years.
Naturally, some search terms or keywords require fresh content or insight. For example, when you’re looking for a hosting coupon code for 2019, it’d be utterly useless to find a coupon code that was generated in 2017 or 2018 and was only good for those years.
Singhal described the categories of keywords that will most likely require fresh content:
Hot trends: These are things that are happening right now, all around the world. Those in the gaming niche usually publish recent or upcoming games for a particular month. Some other keywords for hot trends can be found at Google.com/trends:
A typical example of an authority site that will benefit from a Google freshness reward is Mashable. This popular site constantly publishes fresh content, based on what’s hot in the fields of entertainment, technology, startups, business, education, and politics. Its on-page SEO focuses on gossip or news keyword phrase items.
[amazon box=”B07VJ92G95″ “small”]
Recurring events: Events that take place every month, every quarter, every year, etc., can also lead to an increased freshness score because such content requires constant updating. These keywords are recurring:
- AT&T earnings
- NFL scores
- The Voice contestants
Frequent information update: Some other keywords that are searched for in Google require frequent updates. For example: best dslr cameras and top fitness programs.
These three yardsticks are important to Google when scoring a web page for freshness. But, don’t forget that Google also gauges the freshness of a web page based on the date Google discovered it. Over time, this freshness fades and new content with a newer inception date replaces the older piece.
So, what are you supposed to do for your site, in order to boost its freshness score and ultimately attract more search traffic?
First, you’ve got to consistently publish fresh content.
If you can, publish daily and make sure that you share helpful tips for your target audience. If you’re busy as I am, then publishing two times a week will ensure that your web pages are fresh and attract fresh crawls from Google’s spider, as well as deep bots that will sustain your indexed pages.
Research shows that Google prefers to serve up fresh results to users when they search for a keyword. To get around this preference, some people use blackhat SEO tricks to manipulate web page freshness, by changing the inception date on older articles and pages.
This might work, but it’s very risky and it’s not sustainable. Avoid taking shortcuts that may seem promising. Why would you want to manipulate freshness and inception dates, only to risk your page getting penalized by Google?
Content engagement: The word “engagement,” in this context, means the state of interactivity. The true test of high-quality content is the engagement that it creates. When you’re conscious of engaging your audience, you’ll most likely create the right content for them. Search engines love this.
This initial on-page optimization will align a piece of content with the user’s needs. If you’re going to attract the right clients to your business, you’ve got to focus on engaging your prospects.
Brandon Dennis, of Scotch and Smoke Rings, increased his Facebook engagement by 200%, using Buffer. He created focused news that his audience would enjoy, then shared it with them at the exact time that they wanted it.
He did some research to find out the best times to post on Facebook and Twitter and found this Infographic.

By being consistent with the right social media timing, he increased interactions on Facebook from 150 per day to over 700. That’s a 367% increase in engagement.
Content writing tools: An integral part of on-page SEO is content. You have to give it your full attention. However, you need to automate some writing tasks, because speed matters, when seeking to increase your search rankings. Some of the best tools out there to speed up your content creation are:
HubSpot blog topic generator: This is one of my favorite content writing tools. When you’re stuck and don’t know what to write about on your blog, just enter a few nouns or seed keywords. Then, click on “Give Me Blog Topics!”

HubSpot will generate 5 blog post headline ideas or prompts that will keep you busy for a week. If you want, you could tweak the headline ideas or, if you’re pressed for time, just use them as they are. I find that the prompts are usually attention-grabbing and prepped for search engine success. Take a look at the results:
nTopic: Relevance is a key ranking factor. If you want to make on-page search optimization a lot easier, then your internal links, inbound links and especially your content, all must be relevant to your topic. Link building is another important search engine ranking tool.
However, if you’re not sure whether the topic or keyword that you want to write a post on is relevant, nTopic.org is a simple SEO tool that you can use.
On the homepage, plug your blog URL and topic (e.g., social media marketing) into the appropriate boxes. Click the “score” button.
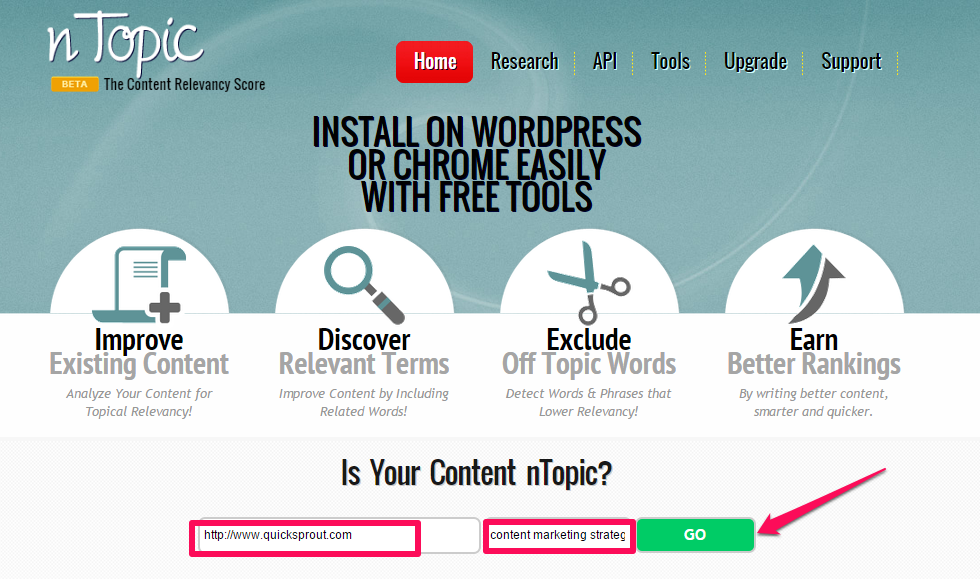
You can find a huge list or other content writing tools here, as well as content marketing tools to make your search optimization efforts more successful.
4. Optimizing Crawlability
SEO is not complicated at all. In fact, people who generate the most results aren’t operating at a higher plane than the rest of us – they simply work harder on the basic elements. SEO boils down to 3 crucial factors:
- Crawlability
- Content
- Link building
If you’re not familiar with “crawlability,” a quick search on Google will help, straight from the Google Knowledge Graph:
You’ve got to recognize that search spiders are not as intelligent as they’ve been portrayed to be by most SEOs.
If your link is broken and spiders couldn’t crawl your web page easily as a result, trust me – they’re not programmed to go looking for the right link. They’ll simply stop there – and you know what comes next, don’t you? Poor performance in the search engine results because of inattention to link building.
SEO was never a “set it and forget it” proposition and it never will be. It’s a continuous learning process, wherein you put yourself in the shoes of your customers and create remarkable content that they want to read.
Remember, remarkable content will only improve your search rankings, if it triggers high engagement and sharing, on both mobile and desktop platforms.
Also, interlinking internal blog pages is an important step towards improving your site’s crawlability. Remember, search engine spiders follow links. It’s much easier for them to pick up your fresh content page from a link on your homepage than by searching high and low for it. Spending time on link building knowing how spiders perform can improve search engine results.
You should also know that there are some case studies pointing to the fact that improving the crawlability of your web pages can boost rankings.
Remember if you have duplicate content on there for a reason, you need to let the spiders know not to index it to then avoid a search engine penalty. Something like a disclaimer on every page might be perceived as duplicate content and needs to be addressed so you still have the right information where you need it and not lose search engine juice.
He made his fresh content easily accessible in one month. Little changes like this could mean a lot in your organic traffic and personal branding.
Having seen the importance of making your content pages easy to find (crawlable), let’s look at some simple ways to go about making it happen.
Your URL Structure: The URL – Universal Resource Locator – is the address of the web page on your site. It’s an important SEO best practice. So, why are there no ultimate guides for structuring your URLs?
Don’t change the URL of your older posts. If you do, it’ll cause a broken link, because your web page will no longer be accessible, when users click the URL that was initially specified.
Blog page URLs are meant to provide some information and meaningful experience to humans and computers alike. This is why we don’t use binary numbers or IP addresses, but rather real words, in our URLs.
Structuring the page URL has been a controversial topic in the blogosphere. Most people believe that you should make it shorter, while others prefer it to be long – like having the whole headline in their URL.
Since the rules aren’t set in stone, the best way to structure your URL is to see how the authority sites are doing it. You can have your category come before the keywords that you’re targeting, the way that HubSpot does:

Or, you can model Copyblogger, which doesn’t use the category for structuring the URL of any web page. Instead, they simply add the 3 keywords that the headline revolves around:
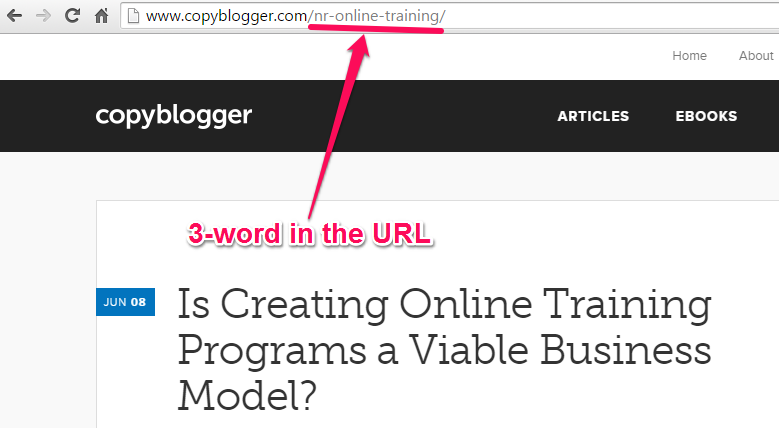
Brent Carnduff recommends that, when you write your URL, you should make it 3 – 5 words separated by a hyphen (-), not an underscore (_).
In all, both long and short, keyword-rich, generic URLs do well in the search engine results pages (SERPs), especially when the content is useful and easy to implement.
Write URLs that will further educate the reader on what you’re talking about. Though I use all my headlines in the page URL, I don’t recommend this because it’s too long for readers to memorize and recall. For example, could you memorize the URL of this post?
It’s much easier for the user to memorize and tell others about this particular web page because the URL is short and contains just the 3 words representing the main topic of the article:
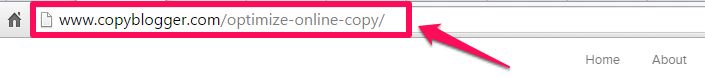
Above all, your URL should first and foremost be self-explanatory. In other words, the user shouldn’t need anyone to interpret what you’ve published on that page. Make it clear and avoid spelling errors.
Crawl Error Resolution: In the process of doing on-page user optimization to attract the attention of search engine spiders, there may be a crawl error encountered.
Remember that the SEO process is one of continuous improvement of your landing pages, content, architecture and audience. So, whatever error you discover, don’t panic – just let it motivate you to do what needs to be done.
If you go to Google Webmaster Tools (now Search Console) and click on the “Health” tab at the top left, then hover over crawl errors, you may see something like this:
These errors typically mean that your web pages were not easily accessible when the bot visited a link to your site or came directly to your site.
It might even be caused by an error in the robot.txt file.
When I say, “come to your site,” I’m not referring to the way people do it. The way bots visit a web page is quite different. That makes sense because they’re advanced programs written to scour the entire web, looking for fresh web page and links to add to their index.
When you find crawl error messages, it means that other sites can’t get access to some of your web pages. This is a mess. The faster you resolve it, the better off you’ll be.
If you get a “not found” error, it can be resolved in a similar manner, with a slight difference.
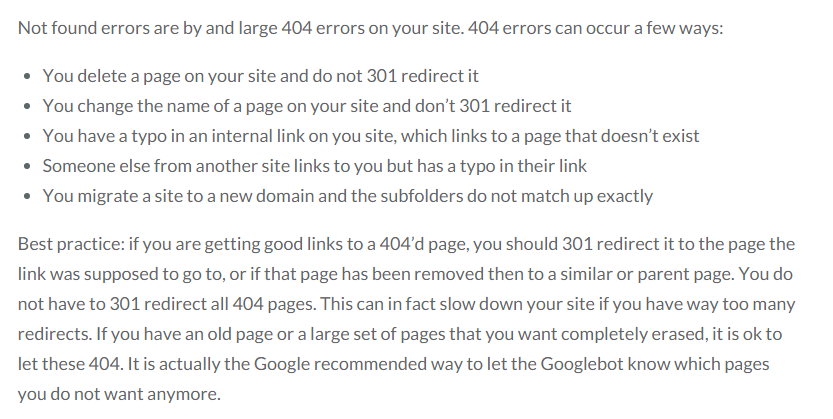
Also Read : most important SEO tips for higer ranking And secrets of article writing
and what is page speed and total guide and what is follow links
5. Mobile-Friendly (Responsive)
When Google Panda was rolled out, many sites didn’t take it seriously. And, consequently, they paid dearly. For example, Ebay lost 80% of its prime rankings. It was a big loss.
The moral of the story: Before a new update jumps out at you unexpectedly, you have to prepare for it.
April 21, 2015 was a happy day for mobile users. Google gave them a gift, by setting up standards that force every site owner to consider mobile users. It was predicted that the update could affect over 40% of Fortune 500 websites.
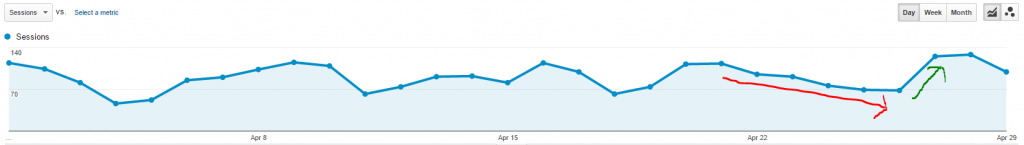
Those who weren’t prepared got dinged in search rankings. One legal software company with a responsive design saw an initial decrease in rankings, but then a substantial rise, a week after:
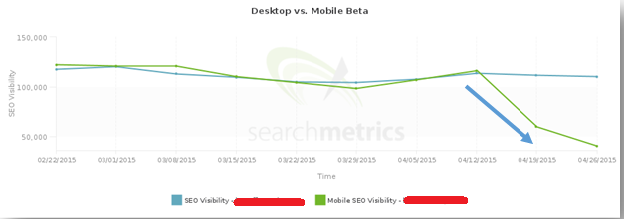
Box Office Mojo, on the other hand, didn’t have a mobile-friendly site. When the update was released, their search rankings and visibility tanked:
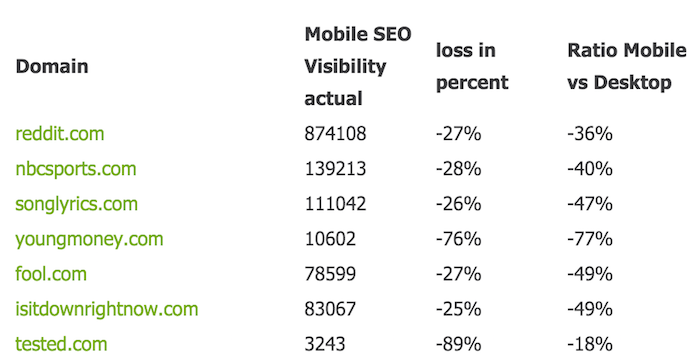
Searchmetrics compiled a list of authority sites that lost and those that gained from the mobile update. Here are some of them:
Trust me, the passion that Google has for mobile users will only increase in the future. That’s because mobile usage is only going up.
The purpose of all of the statistics above is to help you understand the opportunities available with mobile.
The reason why you should include responsiveness as one of your on-page SEO factors to pay attention to is that the majority of your users will access your site from their mobile devices.
You’ve got to layout your site for mobile users. You can always check whether or not your blog/site is responsive, through Google’s mobile-friendliness test tool. Just plug your site URL into the search box, then click the “Test URL” button: