SEO checklist : The complete SEO checklist for optimizing website
SEO checklist
Are you looking for a complete SEO checklist to help drive more traffic to your website?
The 31 points below are based on the principles we believe And our blog traffic has grown significantly over the past 12 months.
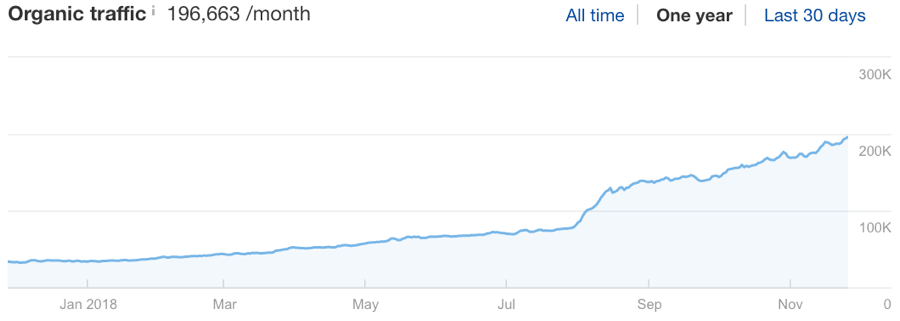
Organic traffic growth for the Ahrefs blog over the past 12 months
Can we attribute 100% of our growth to the application of these principles? We’re not so bold as to claim that.
But we do know one thing:
Most of these principles are applicable to all types of sites: blogs, ecommerce stores, local businesses… everyone.
Sound good? Let’s get started.
How to use this SEO checklist
Think of this checklist like a shopping list of ingredients for a delicious chocolate cake.
You need all the ingredients to make a perfect cake. But some are more important than others.
Forget the chocolate, and your cake won’t be very chocolatey. Forget the optional drizzle of vanilla extract on the other hand and your cake will likely still taste pretty darn good.
What I’m saying is this:
You don’t need to implement everything on this checklist. Just follow the key advice from each subsection and do your best.
That will often be more than enough to outrank the competition.
Basic SEO Checklist
Let’s begin with the SEO best practices that you should employ before doing anything else.
Note that these things are unlikely to have a direct effect on rankings. They’re just the basics that every website owner should have in the bag.
[amazon box=”B07NWCFMFQ” “small”]
1. Install Yoast SEO (or a similar SEO plugin)
Yoast SEO is a free SEO plugin for WordPress and a few other CMS’.
Functionality-wise, it does a lot—create sitemaps, optimize metadata, apply “noindex” attributes to specific areas of your site, and much more.
In other words, it makes the daunting technical stuff less daunting.SIDENOTE. All in One SEO Pack and The SEO Framework are other popular Yoast alternatives for WordPress.
If you’re not using WordPress or any of the other CMS’ supported by Yoast, then head over to Google and look for the “best SEO plugin for [your CMS].”
2. Create a sitemap
Sitemaps tell search engines where to find the important content on your site (which they can then crawl and index).
Here’s what they look like:
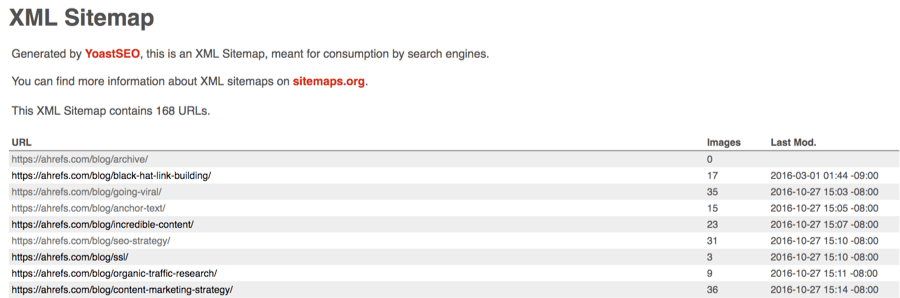
You can usually find yours at yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml.
How do you create one? If you’re a WordPress user, use Yoast. Otherwise, there are many sitemap generators around—Google it!
3. Create and add a robots.txt file to your site
Robots.txt is a plain text file that instructs search engines where they can and can’t go on your site. It will look something like this:
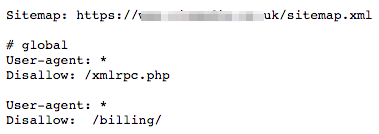
You can see that this particular robots.txt file includes a link to the sitemap (which tells search engines where to find it) followed by some directives instructing search engines not to crawl or index any web pages with “/billing/” in the URL.
WordPress users can use Yoast to create and optimize their robots.txt file. This robots.txt generator works well for non-Wordpress users.
Read this guide to learn everything you need to know about robots.txt.PRO TIP
Check to see if you already have a robots.txt file on your site by navigating to yourdomain.com/robots.txt.
4. Install Google Analytics
Google Analytics is a free tool from Google. It lets you see how many people visit your site and how they interact with it.
To install it, sign up and paste the supplied tracking code into your website.
Read this guide if you’re not sure how to do that.
Also read : Seo top keyword reasearch tools And Long tail keywords complete guide
5. Setup Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a powerful, must-have tool for all webmasters.
It lets you track your performance in search and see the keywords for which you rank.
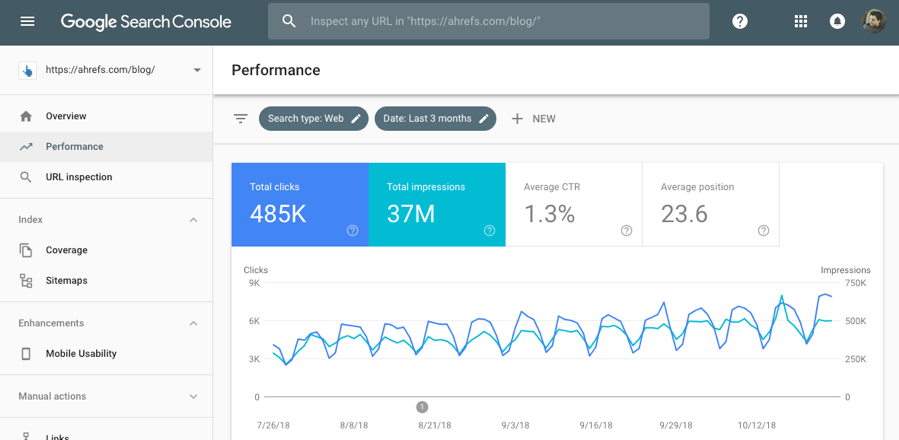
It will also keep you in the loop about on-site improvements you can make.SIDENOTE. It’s also worth signing up for Bing Webmaster Tools—which is essentially Bing’s equivalent of Google Search Console.PRO TIP
Link Google Search Console with Google Analytics to see Search Console data in Analytics.
You can learn how to do that here.
[amazon box=”B07NWCFMFQ” “small”]
Keyword Research Checklist
Keyword research is perhaps the most crucial piece of the SEO puzzle.
After all, if you don’t know what people are searching for, how can you possibly optimize your content for search engines?
Follow these checklist items to get off on the right foot.
1. Find a primary keyword to target
Each page/post on your website should target one main primary keyword.
That’s what we do with all posts on the Ahrefs blog.
- The State – Most Actionable SEO Tips → “SEO tips” (10K searches/month)
- Long-Tail Keywords: The ‘Secret’ to Getting TONS of Search Traffic → “long tail keywords” (9K searches/month)
How do you find the right primary keyword to target?
Use tools like Google Keyword Planner and Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer.FURTHER READING
2. Find long-tail keyword variations
People search for the same thing in different ways. So much so, that 15% of Google searches are new and have never been searched before.
That’s why it’s important to optimize for long-tail keyword variations.
The easiest way to find such keywords is to use Google autocomplete. Type your primary keyword (e.g., “SEO checklist”) into Google, and you’ll see long-tail suggestions like so:
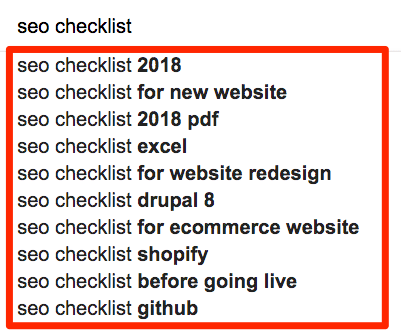
You can also use the Search Suggestions report in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer to find even more long-tail suggestions.
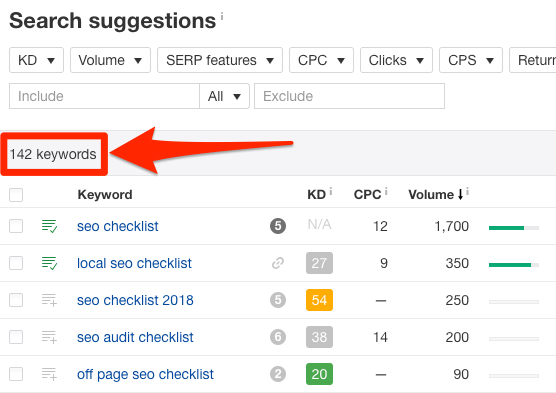
Read our full guide to long-tail keywords to learn more about finding and optimizing for them.
3. Understand ‘search intent’
How often do you Google something and are unable to find what you were looking for within the first few results? Hardly ever, right?
That’s because Google is very good at understanding search intent—i.e., what the user is looking for when they type some words into their search engine.
To have any hope of ranking for a particular keyword, you need to do the same. You must understand the search intent behind the keyword you’re targeting.
Looking at the current ranking results in the SERPs can help you figure this out.
Let’s do this for “SEO checklist.”
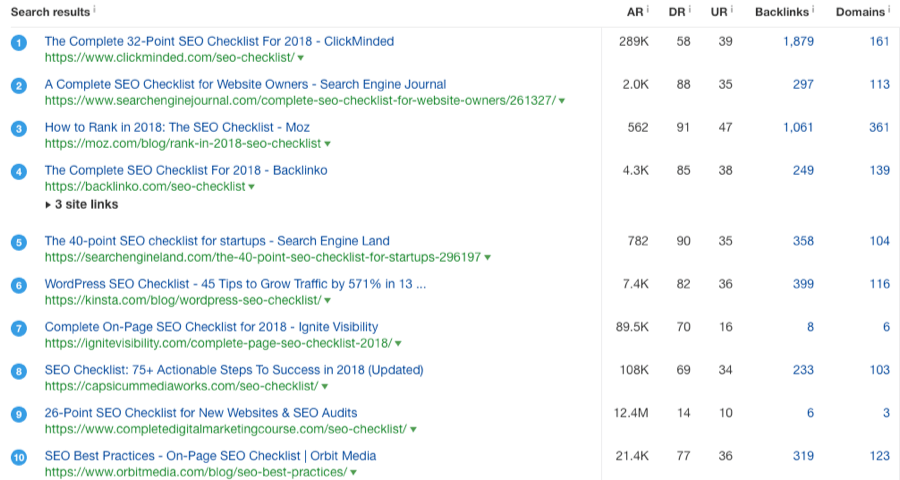
Top 10 search results for “SEO checklist” via Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer.
Here, all the results are blog posts. There are no product pages or ecommerce results because that’s not what people want to see.
So if you had a page advertising an SEO checklist for sale, it would be almost impossible to rank.
You can also look at the ranking history of the top 5 ranking pages in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer to further your understanding of search intent.
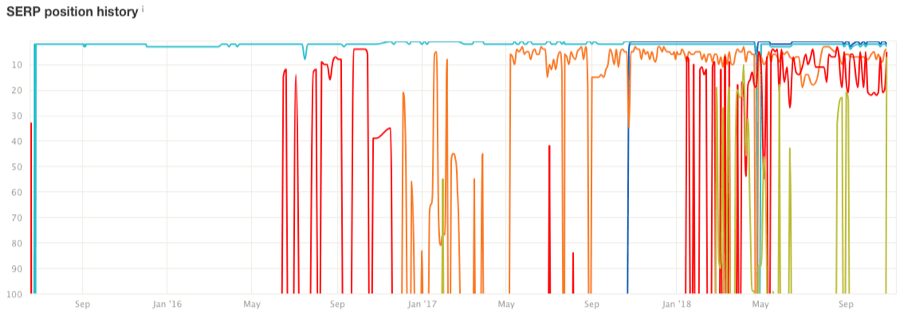
Volatile SERP position history via Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer
Do you see that the top-ranking pages are volatile and jump around often? Google may not be sure what users want to see.
If results are pretty stable, then search intent is clear.
4. Delve deeper into the questions people are actually asking
Let’s say that someone Google’s the phrase “SEO.”
You can see from analyzing search intent that this is an informational query where users are looking for information/tutorials/guides.
But what specific questions do they have? What information should you include in your content?
Look at the “People also ask” box in the search results to get some ideas…
… along with the “Searches related to” section at the bottom of the page:

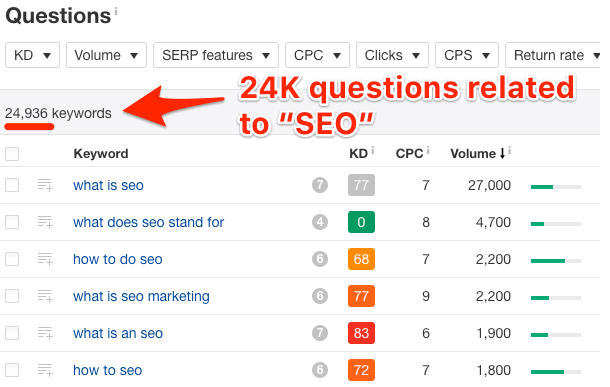
You can also use the Questions report in Ahrefs’ Keywords Explorer to see more related questions.
5. Make sure that ranking for your chosen keyword is an achievable goal
Nothing is worse than pursuing an unachievable keyword.
Of course, no keyword is truly unachievable. However, some are pretty damn close to impossible to crack, especially if you’re competing with strong pages.
You can get a sense of keyword difficulty by looking at Ahrefs’ Keyword Difficulty score.
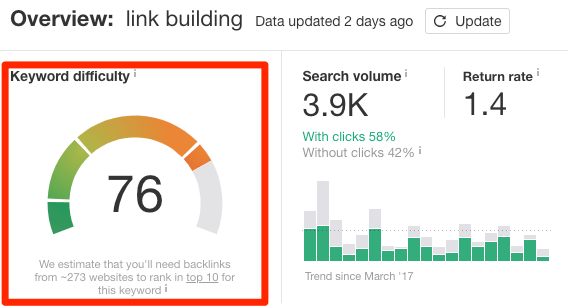
But don’t rely on that entirely. Check the SERPs yourself. Things that may indicate a difficult keyword to crack include:
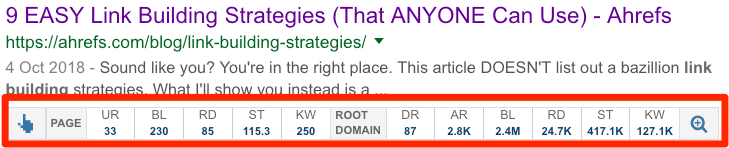
- Lots of referring domains to the top-ranking pages;
- High URL Rating (UR) to the top pages;
- Big brands in the top 10.
Found a challenging keyword? Consider pursuing an easier keyword/topic instead. You should always target keywords within your wheelhouse.
[amazon box=”B07H97FRX5″ “small”]
On-Page SEO Checklist
Keyword research = DONE.
Your next job is to optimize the actual content on your page—i.e., on-page SEO.
Let’s do it!
1. Use short, descriptive URLs
Pages with shorter URLs rank better—that’s according to our 2016 study of 2 MILLION keywords.
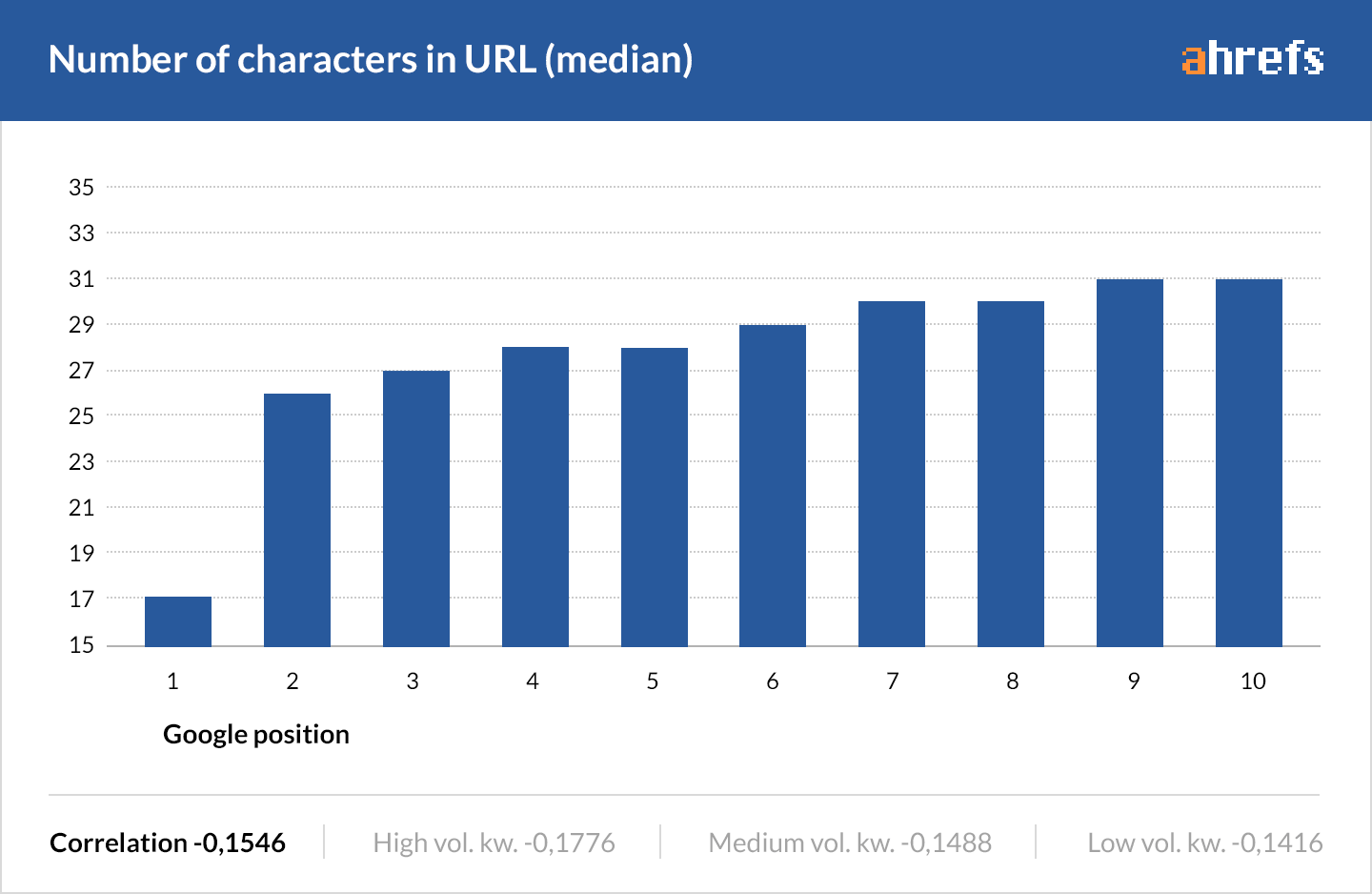
SIDENOTE. Keep in mind that this is a correlation study. Correlation ≠ causation.
But don’t sacrifice descriptiveness for length. Your URLs should offer some insight into what the user should expect when they click through to the page.
Example: https://ahrefs.com/blog/free-seo-tools/
This URL makes it clear what to expect from this page—i.e., a list of free SEO tools.
Here’s another benefit of using descriptive URLs: They tend to include your target keyword.
2. Write a compelling title tag and description
Most people tell you to add your target keyword to your title tag and meta description.
Is that bad advice? Not at all.
It’s good practice. But don’t sweat it if it doesn’t make sense to do so.
Most of the pages ranking on the front page of Google don’t have an exact-match keyword in their title tag. That’s according to our 2016 case study of 2M keywords.
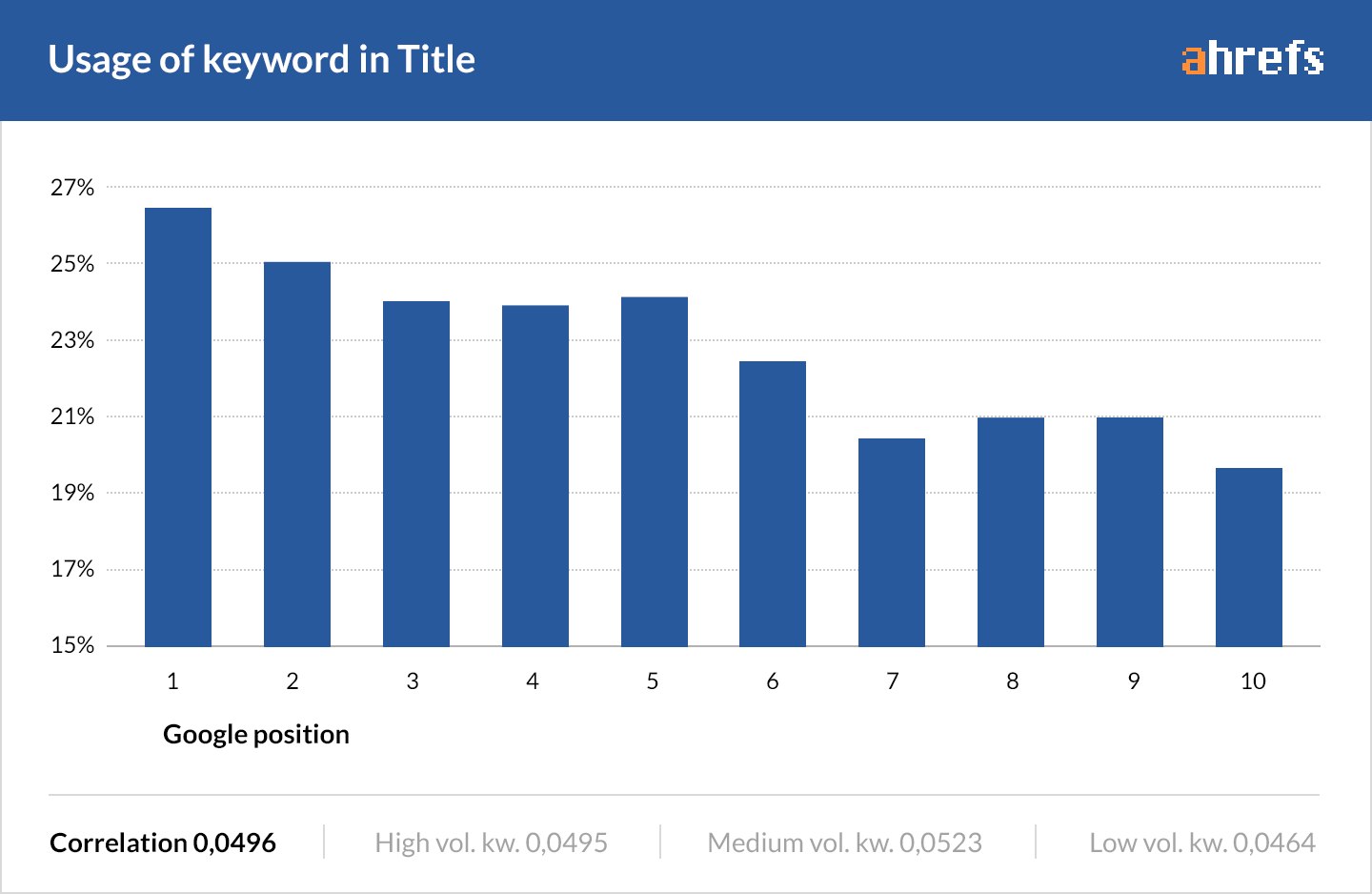
The same is true for meta descriptions.
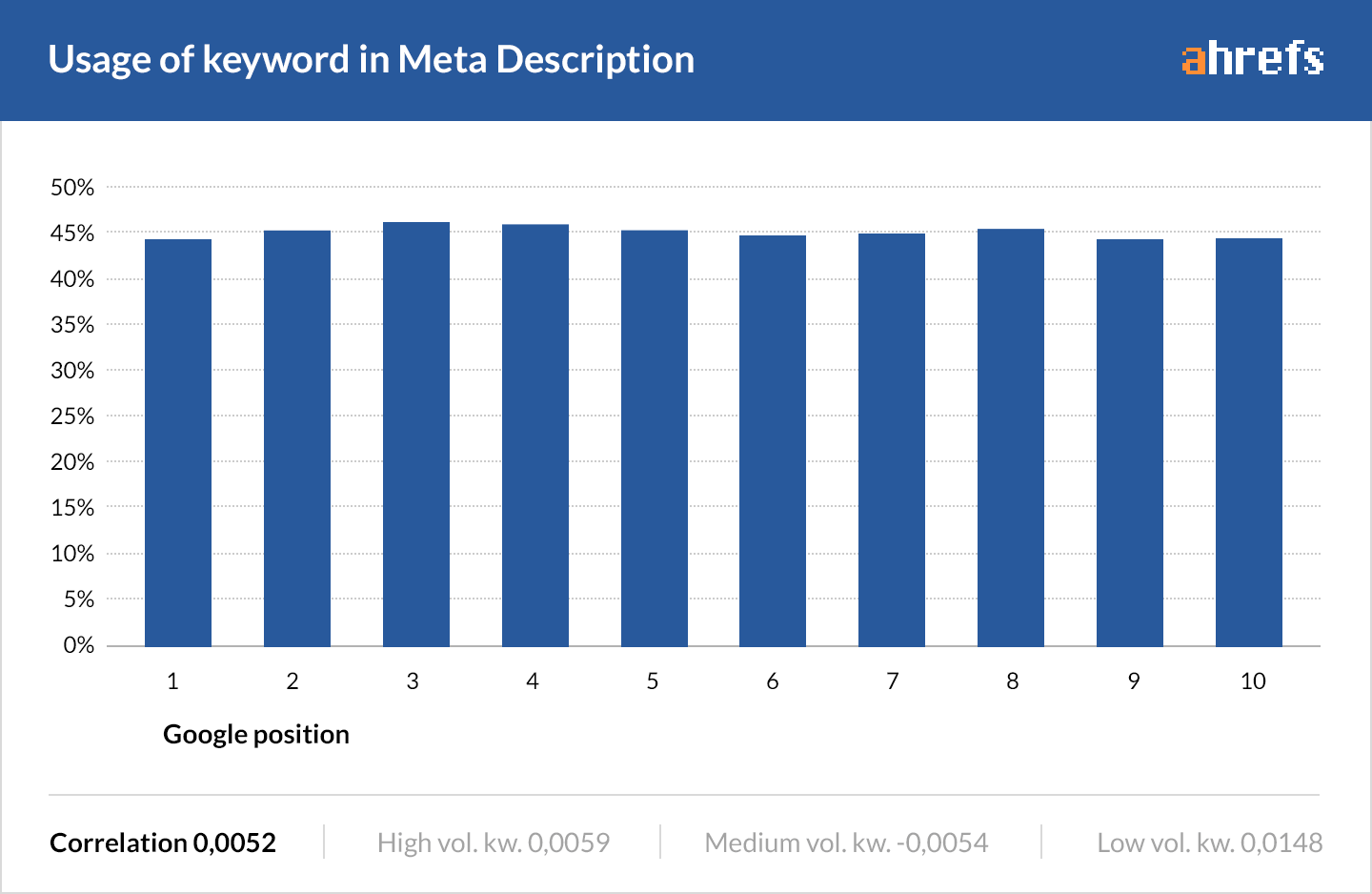
Your primary goal shouldn’t be to shoehorn keywords into such places. Instead, work to craft an enticing title and description that will increase CTR and bring more traffic to your website.
Also Read : most important SEO tips for higer ranking And secrets of article writing
3. Use one H1 on your page (and include your keyword in it)
Google recently stated that it’s okay to use as many H1 tags on your page as you want.
But we think it’s still good practice to use just one.
That’s because H1’s are typically used as a wrapper for the title of the page—and a page can surely only have one title.
But what about keywords? Should you include your target keyword in there?
According to our 2016 study of 2M keywords, ~85% of top-ranking pages don’t have their keyword in the H1 tag.
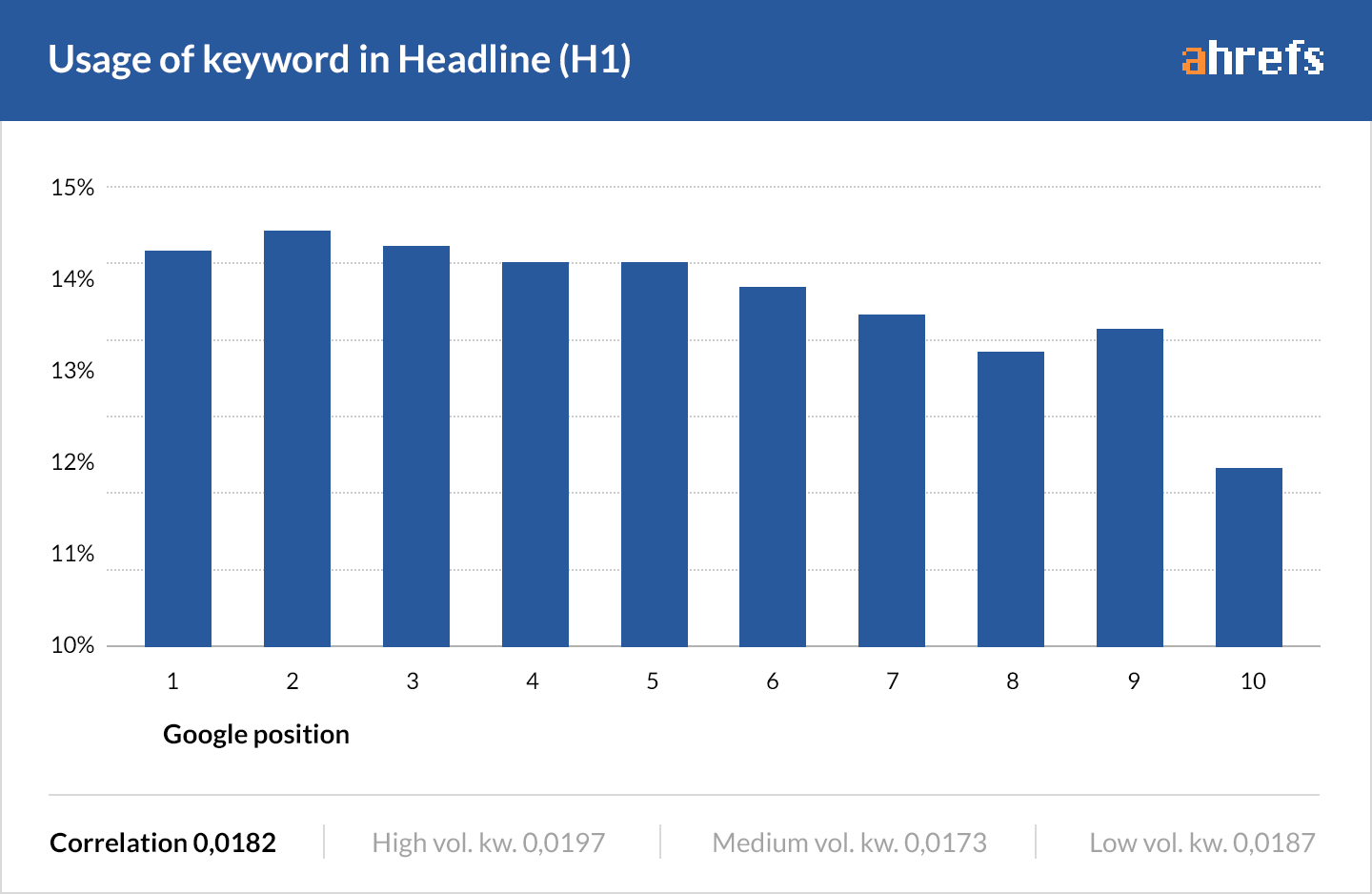
Still, there are two important reasons to include your keyword here:
- Scannability. Having your keyword in the H1 helps to reinforce that the visitor is in the right place. It makes it clear that your content tackles the topic they likely Googled before arriving on your page.
- Link framing. People will often link to your page using the title. Including your keyword in the H1 will increase your chance of receiving links with your target keyword in the anchor text.
If you want to quickly check whether there are any pages on your site with multiple H1’s, you can do so with Ahrefs’ Site Audit.
Watch this video to learn more.
4. Link to relevant internal and external resources
Web pages that link out to high-DR resources rank higher than those that don’t.
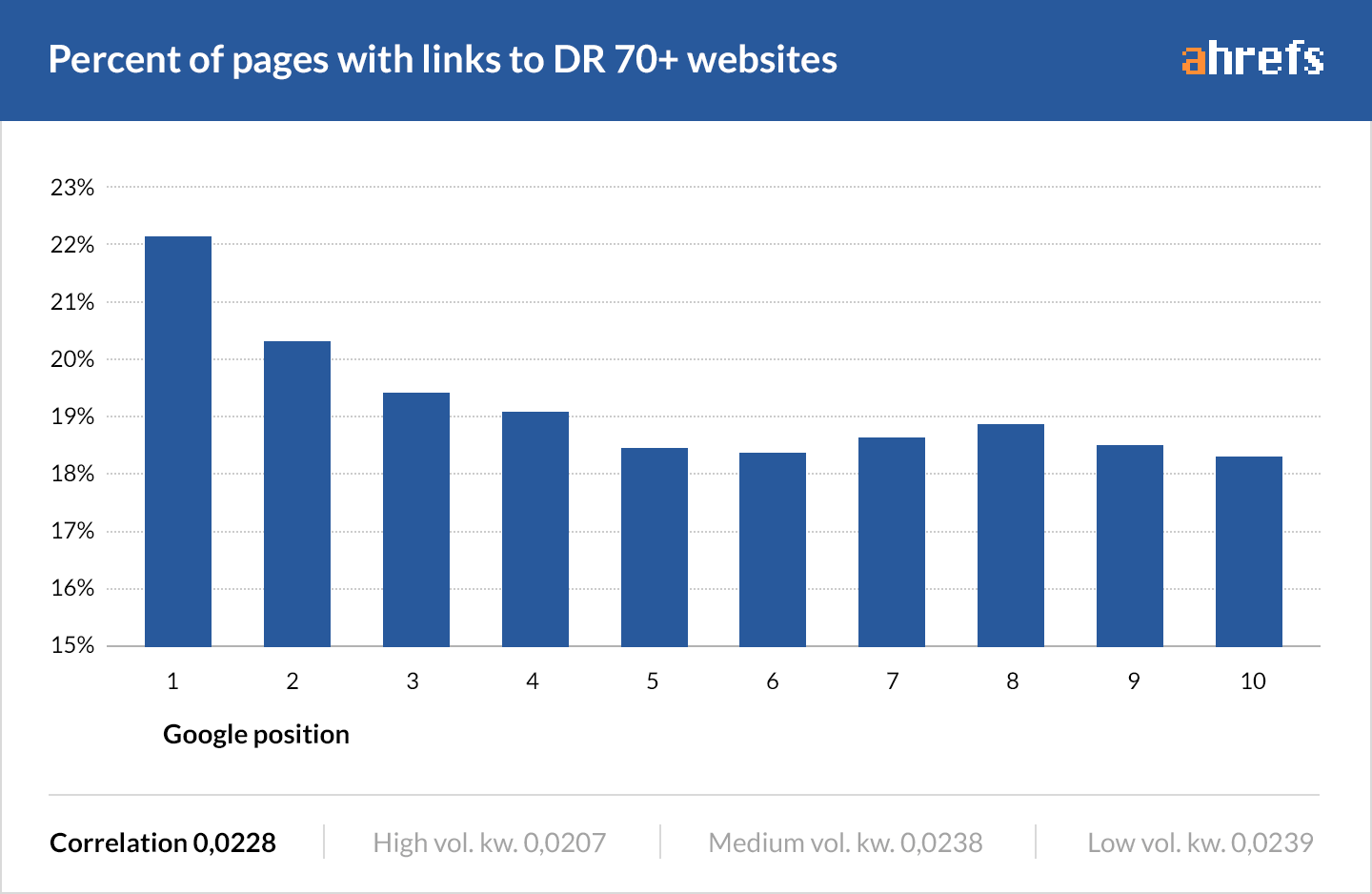
IMPORTANT: That is the result of a correlation study. It doesn’t imply causation.
You should, therefore, not be afraid to link out to other web pages. Just make sure you link to high-quality, relevant stuff.
Internal links are also important.
Whenever you publish something new, make an effort to add internal links from relevant places on existing pages.
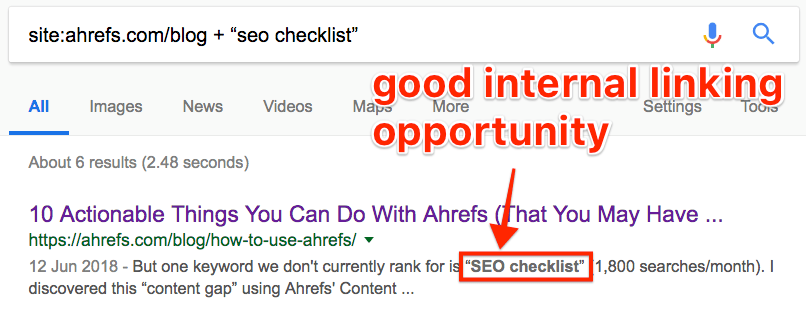
How do you find such pages? Google site:yourdomain.com + “topic”
For example, if we wanted to find relevant places on ahrefs.com from which to link to this article, we could do so by Googling site:ahrefs.com/blog + “SEO checklist”
5. Optimize your images with descriptive “alt” tags
70% of top-ranking pages don’t have their target keywords in any of their image alt tags.
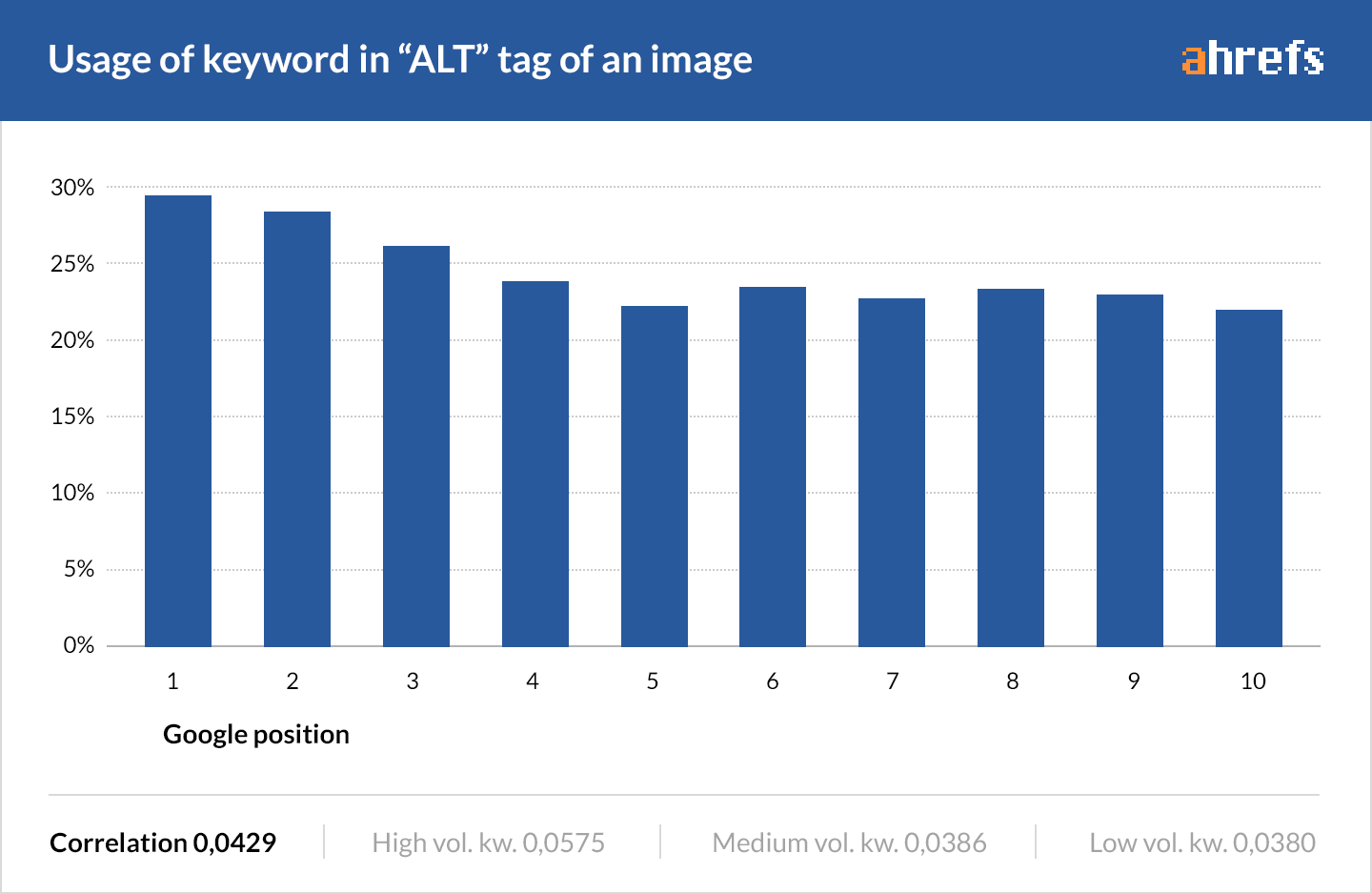
50% don’t even have their alt tags filled in.
So alt tags aren’t particularly important then, right?
Not so fast. Remember that the purpose of alt tags is to offer some context to the reader should the image fail to load (or if the visitor is using a screen reader).
For that reason, you should make sure alt tags are descriptive—this will often result in the natural inclusion of your target keywords.
Alt text is also helpful for ranking in Google Images.
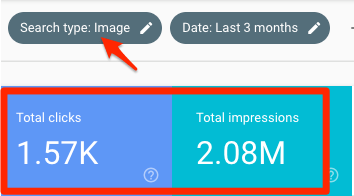
How important is Google Images?
According to Google Search Console, we’ve had over 2 million impressions and 1.57K clicks to our site from Google Images in the past three months.
Being as adding alt text only takes a few seconds, it’s well worth doing.
6. Intelligently “sprinkle” long-tail variations throughout your content
Did you know that the average top-ranking page also ranks for almost ~1K other keywords?
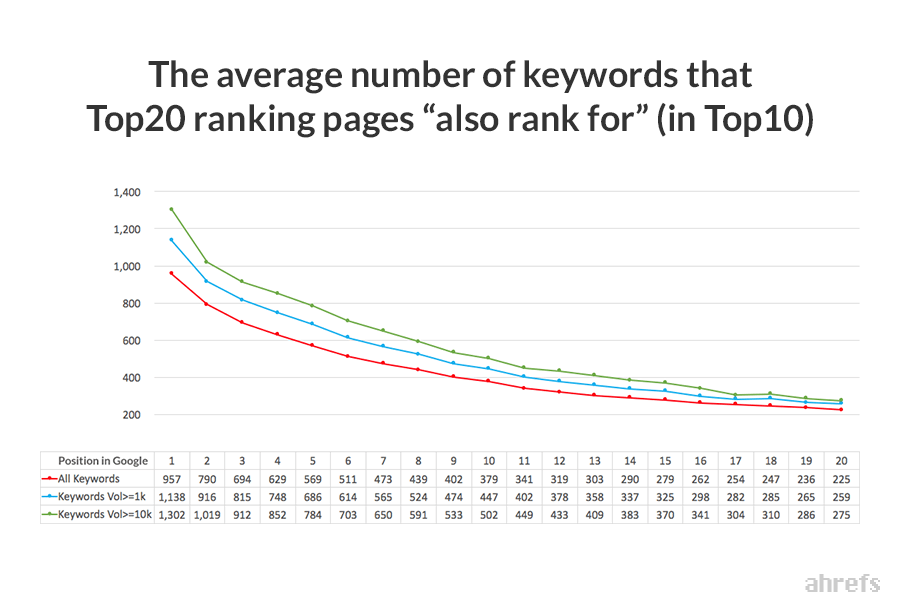
This means that most of the time, the bulk of your traffic won’t come from your primary target keyword—it’ll come from long-tail variations.
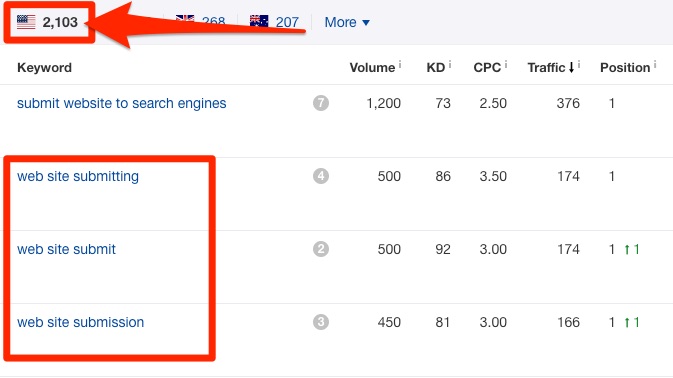
That post gets 6.5K monthly visitors from the US according to Ahrefs’ Site Explorer.

But our target keyword only has a search volume of 1.2K and sends 376 visitors per month to our site. The bulk of the traffic to that page actually comes from the 2,100+ long-tail variations.
It’s for that reason that it’s important to optimize for long-tail variations too.
Doing this is easy. Sprinkle them throughout your content wherever they make sense. Just don’t overdo it or shoehorn keywords where they don’t belong—the readability of your content should always take priority.
[amazon box=”B07H97FRX5″ “small”]
7. Add schema markup to enhance SERP visibility (where relevant)
Schema markup helps search engines to better understand your content. But it can also dramatically affect how your page is displayed in the SERPs.
Here’s a page with schema markup that currently ranks for “pizza dough recipe:”
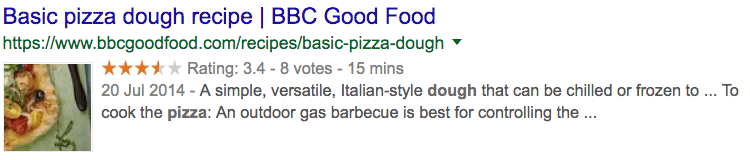
Here’s what it would look without schema markup:

Do you see the difference?
Schema markup can increase click-through rates and bring more traffic to your website.
It’s not that technical to implement either. Use Google’s markup helper or this Schema markup generator to do it with ease.
Content Checklist
Picking a topic with high search traffic potential and doing some basic on-page SEO is important, but all your efforts will be in vain if your content isn’t up to scratch.
Follow these quick tips to level-up your content.
1. Write a kick-ass intro
Fail to convince readers that your page offers what they want within a few seconds and they’ll hit that back button faster than you can say “dwell time.”
This is known as “pogo-sticking.”
Your best defense against this is a compelling intro.
Good introductions should do three things:
- Resonate with the reader;
- Build trust;
- Promise a solution to the user’s problem.
But is “pogo-sticking” even a Google ranking factor?
Here’s what Google’s John Mueller had to say on the matter:We try not to use signals like that [pogo-sticking] when it comes to search.

John Mueller, Webmaster Trends Analyst Google
Interesting. But even if it’s not a direct ranking factor, there’s one other reason that a compelling intro is still important for SEO:
Nobody is going to link to your content without reading it in the first place.
So, to attract links—which many studies have found to correlate heavily with rankings and traffic over the years, including our own—the reader first has to be engaged enough to read your content.
That’s why your introduction is arguably the most critical part of your page.
2. Focus on readability
Nobody wants to read a big wall of text.
That’s why you should always break up your content with subheadings, images, quotes, etc.—anything that will keep the reader glued to the page.
We even use images in our intros to create the illusion that we’re getting stuck straight in, rather than wasting our readers’ time with a lengthy intro.
3. Use short sentences and paragraphs
50% of the US population read below an 8th-grade reading level.
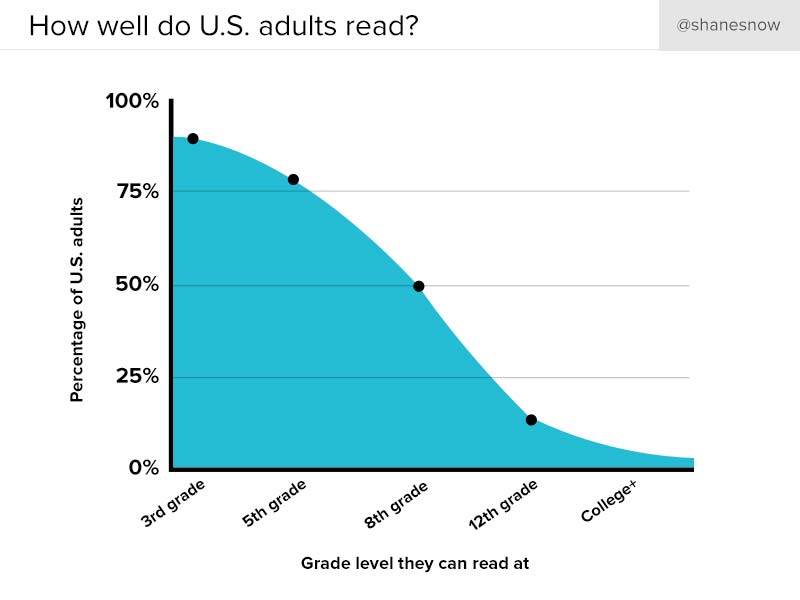
So unless you want to alienate half of the population, don’t overcomplicate things.
That means using short sentences and paragraphs. Also:
- Avoid unnecessary jargon;
- Use simple words instead of complex ones;
- Remove excruciatingly unnecessary adverbs.
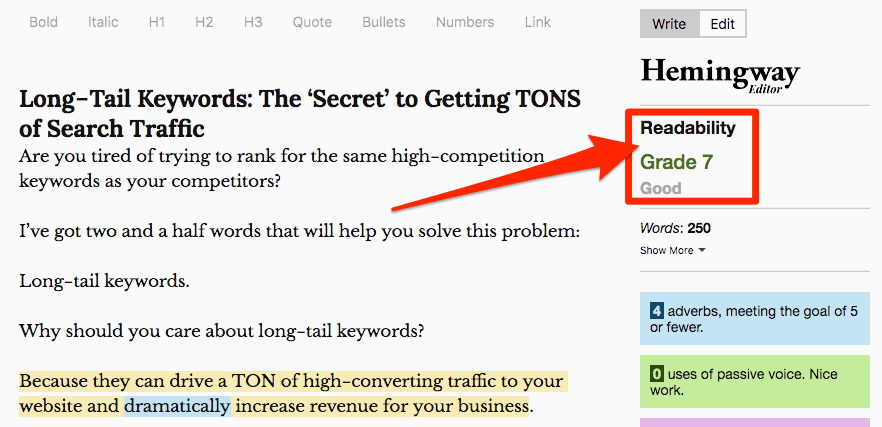
Hemingway is a free, browser-based tool that will help simplify your writing. It tells you the current grade level of your copy and suggests improvements.
4. Create the best piece of content on the topic
How do you create the best content on a given subject when it’s so subjective?
Answer: E‑A-T.
Confused? E‑A-T stands for Expertise/Authoritativeness/Trustworthiness. That is what Google claims to be looking at in their official search quality evaluator guidelines.
Here’s a more in-depth look at the three critical attributes of E‑A-T, taken from those same guidelines:
- The expertise of the creator of the MC*.
- The authoritativeness of the creator of the MC, the MC itself, and the website.
- The trustworthiness of the creator of the MC, the MC itself, and the website.
* MC stands for main content.
Learn more about these guidelines in section 3.1 here.
Technical SEO Checklist
It’s not uncommon for technical SEO issues to hold a website back from ranking as high as it deserves.
The problem: Most people think technical SEO is daunting and complicated.
The good news: It doesn’t have to be.
You can learn how to do a full SEO audit in this post (or in the video below).
However, as this post isn’t solely focussed on technical SEO, what follows are a few common and easily solvable technical SEO issues.
[amazon box=”B07H97FRX5″ “small”]
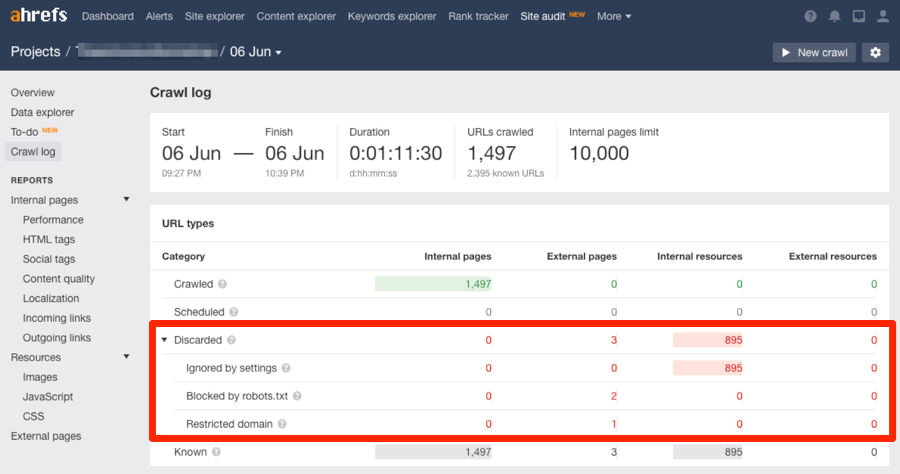
1. Identify (and FIX) any crawl errors
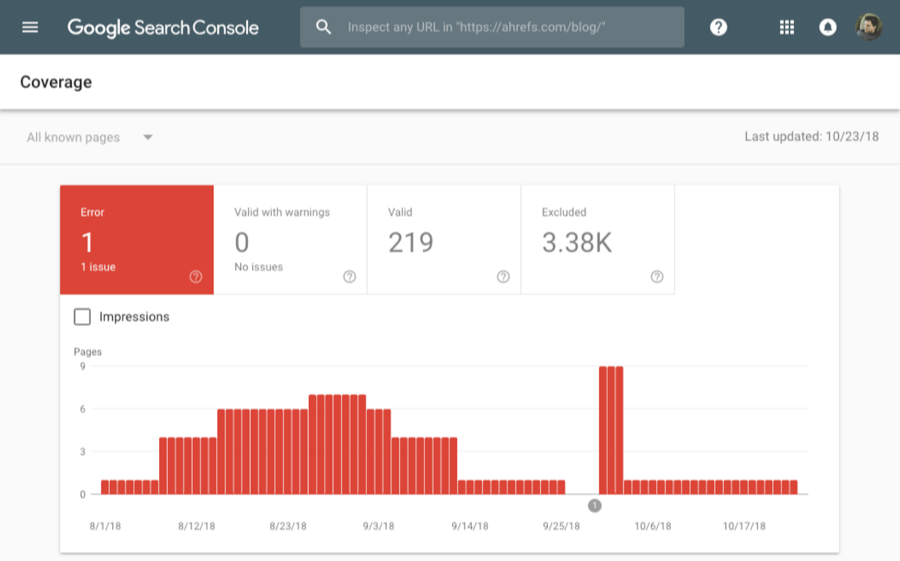
Crawl errors mean that Google is having trouble viewing the content on your site.
If they can’t view it, they won’t rank it. It’s as simple as that. That’s why you should fix such issues as soon as possible.
You can find crawl errors in Google Search Console > Coverage.
SIDENOTE. If you’re using the old version of Google Search Console, you can find crawl errors in Google Search Console > Crawl > Crawl stats.
You can also find crawl errors (e.g., web pages and images blocked by robots.txt) using Ahrefs’ Site Audit.
2. Make sure your site loads FAST
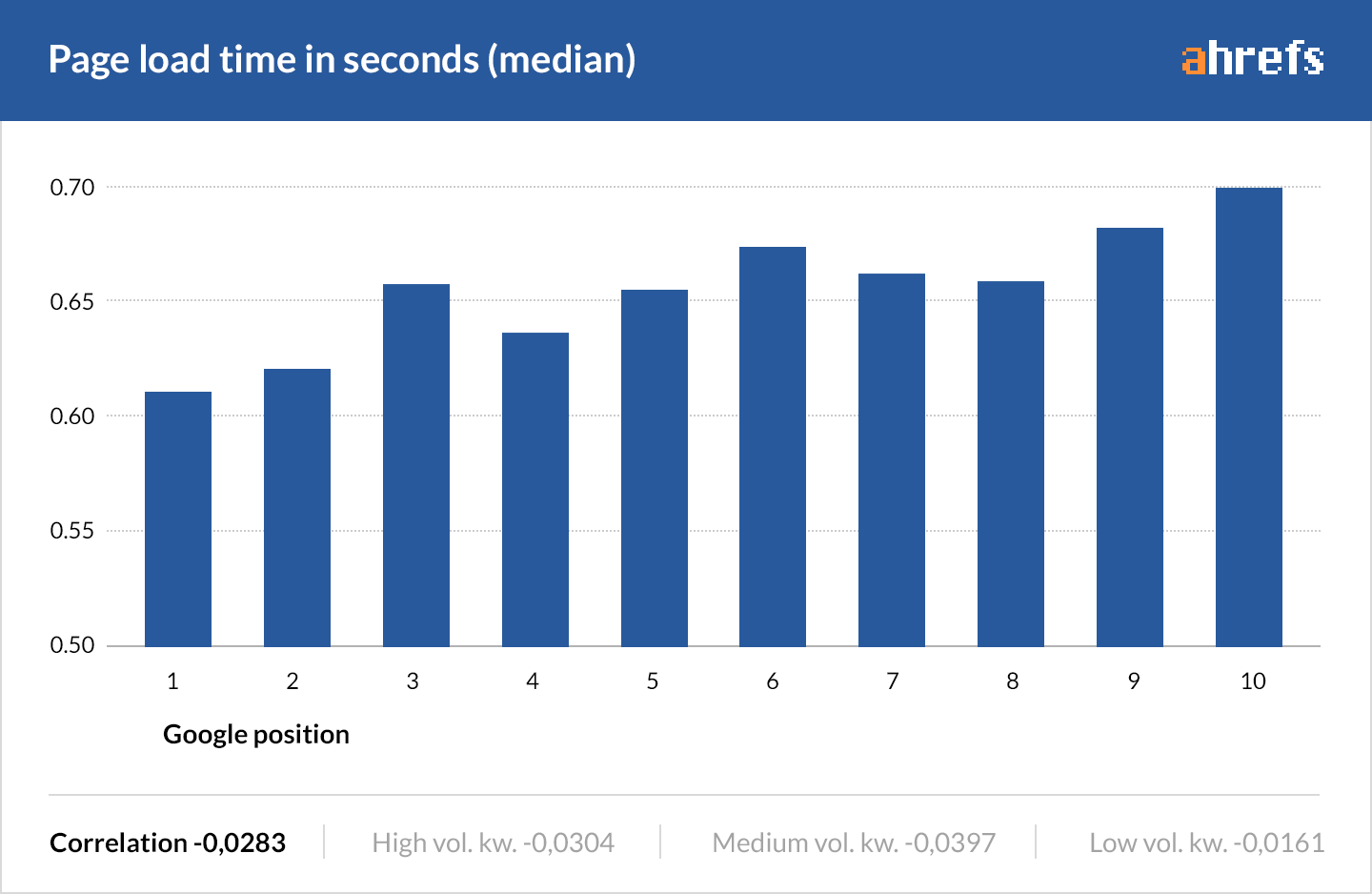
Page speed is the talk of the town in the SEO world right now.
But our 2016 data only shows a small correlation between fast-loading pages and higher rankings.
However, regardless of what the data says, you should still make sure that your site loads fast.
Why? Because it’s damn frustrating to click on a search result and have to wait for ages for it to load. So frustrating, in fact, that most people don’t do it. They just hit the back button and click a different result.
Not only does this result in you losing out on visitors, but it’ll also wreak havoc on engagement metrics such as time on page and dwell time.
You can use GTMetrix to see how fast your web page loads.
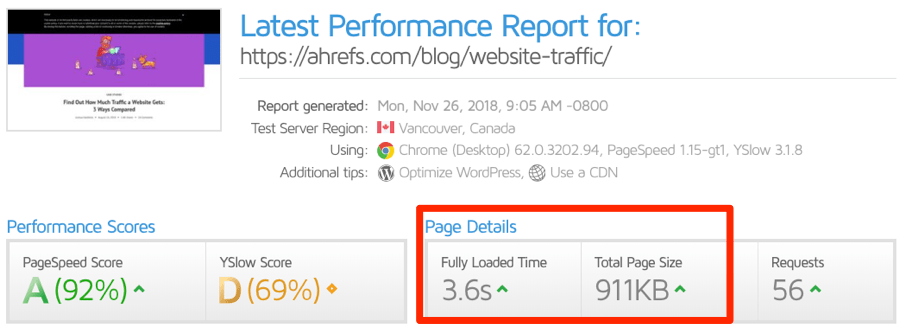
Page speed can be complicated. So as a general rule, I would aim to keep the Fully Loaded Time below 3 seconds. (You can see that we have work to do ourselves!)
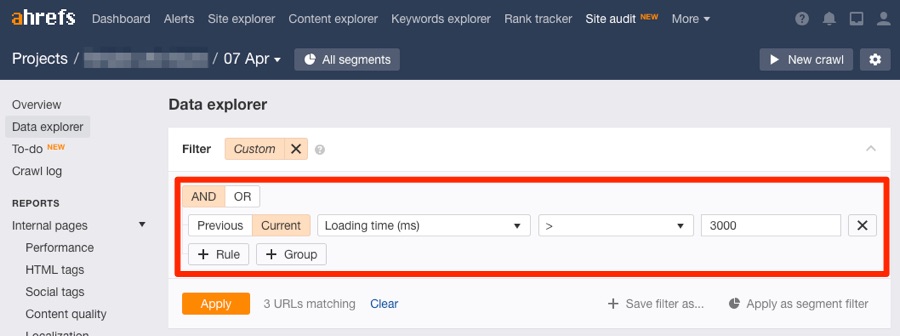
You can find all pages on your site where this isn’t the case using Ahrefs’ Site Audit.
Site Audit > Data Explorer > Loading time (ms) > 3000
3. Fix outbound broken links
According to our 2016 study, ~2% of pages that rank in the top 10 have broken links.
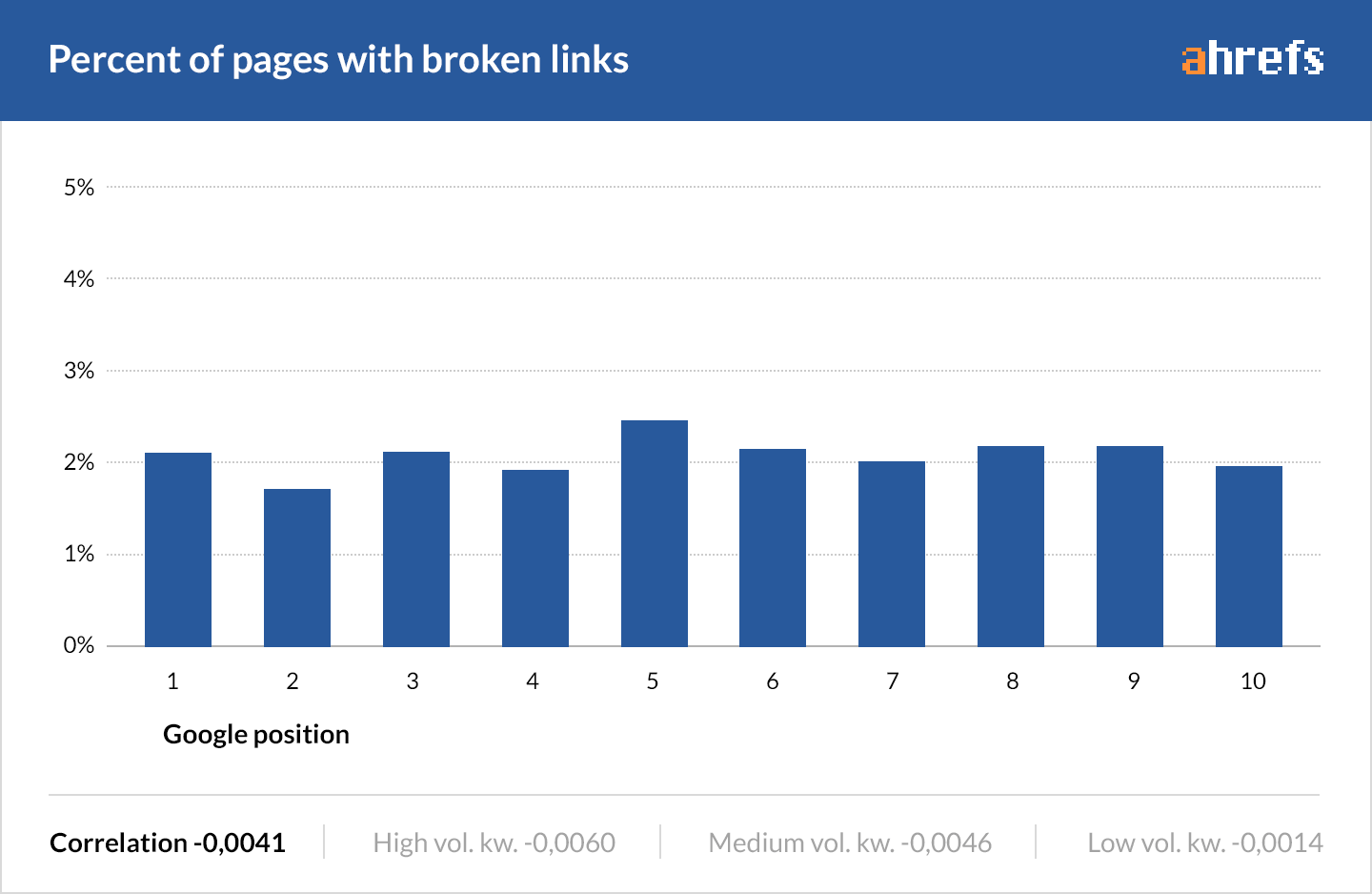
Does this mean that the presence of broken links on a page is a ranking factor?
Not exactly. But the fact remains: broken links are bad for user experience. And user experience is something that Google cares deeply about—that’s why they adjusted their algorithm to go after sites with too many distracting ads a few years ago.
Furthermore, broken internal links waste “link juice,” which can have a direct adverse effect on rankings.
4. Make sure your site is mobile-friendly
Most searches take place on mobile devices as opposed to desktop. So having a mobile-friendly website is more important than ever.
Check whether or not your site needs work with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
Fix any issues with mobile-friendliness as a priority.
5. Switch to HTTPs
HTTPs is a ranking factor. Google said so.
However, 80% of top-ranking sites are still not secure (according to our data).
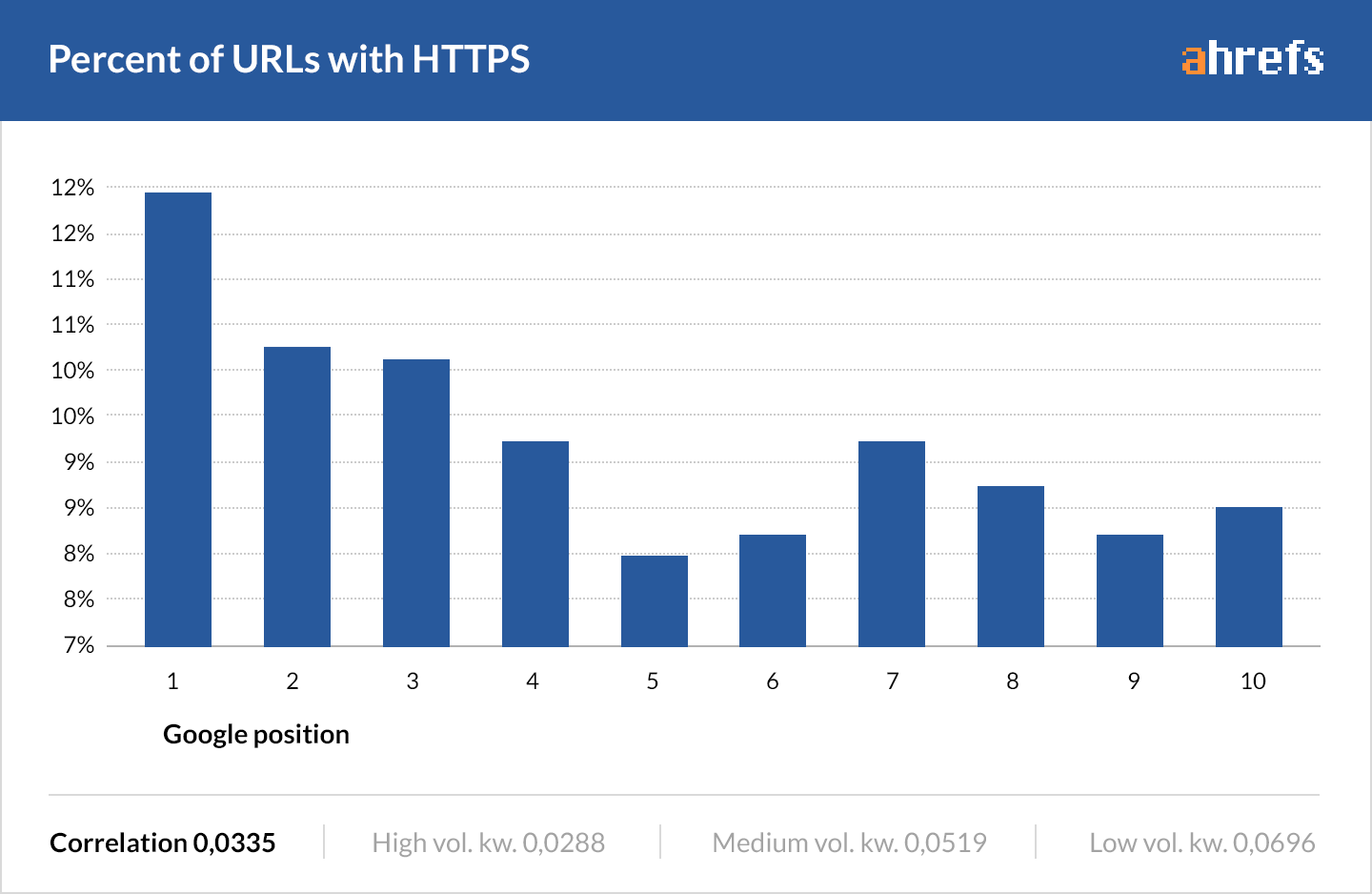
But that study was conducted in 2016, so I’d urge you to take it with a pinch of salt.
More and more sites are switching to HTTPs, and so should you.
Potential ranking boosts aside, HTTPs will protect your visitors’ data. This is especially important if you have any contact forms on your site. If you’re asking for passwords or payment information, then it’s not just important, it’s an absolute must.SIDENOTE. You can get a free SSL certification from Lets Encrypt
6. Fix duplicate content issues
Duplicate content occurs when you have two or more similar or identical pages on your website.
This can cause problems as Google may not know which of the pages, if any, should rank.
It’s a common ecommerce SEO issue thanks to faceted navigation. That alone can cause hundreds of duplicate content issues because of URL parameters.
You can find duplicate content issues with Site Audit
Run a crawl and go to Content Quality > Duplicate pages without canonical
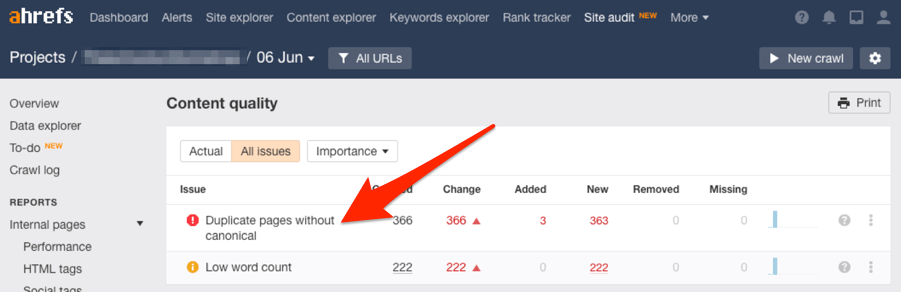
Fix these by canonicalizing the affected pages to a “master” page.
Link Building Checklist
Link building is perhaps the most challenging SEO task.
That’s because not everything is within your control. You’re often reliant on other people giving you links as a result of your outreach efforts.
So here are a few tried and tested link building tactics you can use:
1. Replicate your competitor’s links
Your competitors’ likely have at least some backlinks.
Believe it or not, that’s a good thing. If a website is linking to your competitor, chances are it’d make sense for them to link to you too.
Conclusion: You can build links to your site by replicating your competitors’ links.
How? There are many different ways. However, one quick win is to find sites that are linking to multiple competitors as the chance of them also linking to you is high.
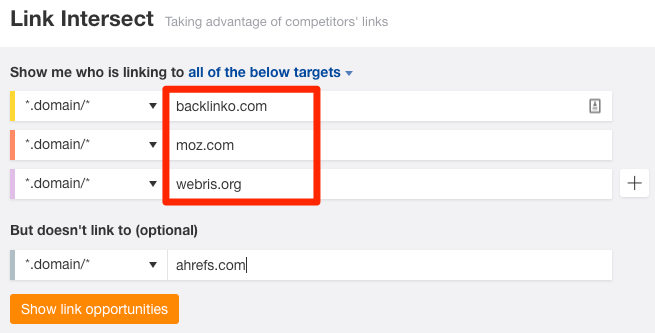
… then hit “Show link opportunities.”
Look for links that may be easy to replicate, such as those from guest posts, link roundups, forums, directories, etc.
2. Monitor and reclaim any lost links
Diamonds are forever. Links aren’t.
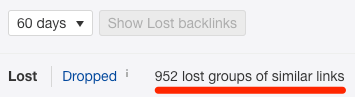
Links disappear like this for all kinds of reasons. Sometimes they’re gone for good. Other times it’s possible to reclaim them.
What are the easiest ones to reclaim?
Links marked as “link removed” in Ahrefs.
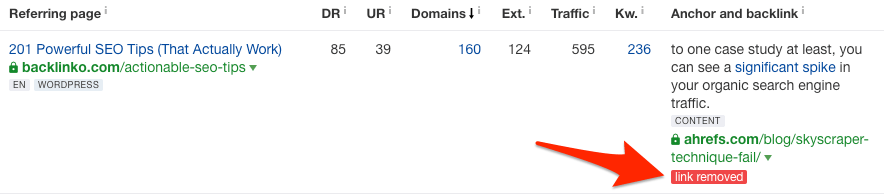
These are links that the author decided to remove from their page.
So your job is to figure out why that was and give them a compelling reason to reinstate the link (or a link to another relevant resource).
Learn more about how to easily find and reclaim lost links in our full guide to link reclamation.
3. Pursue unlinked mentions
People will sometimes mention your brand—or things related to your brand—without linking back to you. These are known as unlinked mentions.
Here’s an example of one:
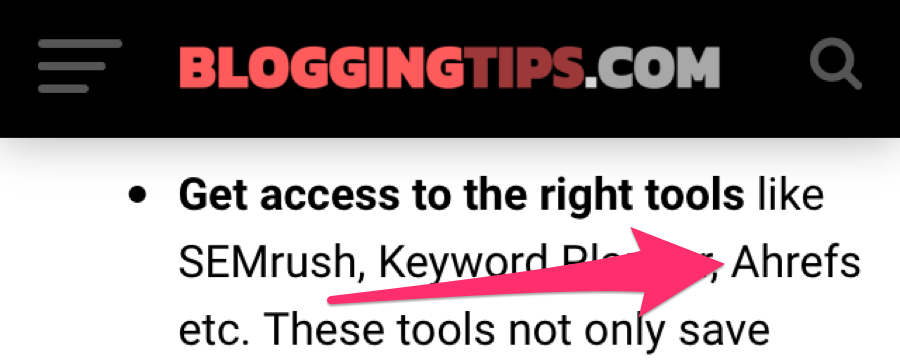
You can see that even though they mention Ahrefs, they don’t link back to us.
Now, wouldn’t it be cool if you could convert unlinked mentions for your brand to linked mentions?
It would, and you can. Just reach out to the authors and request that they “make the text clickable.” Because they’re already familiar with your brand, there’s a high chance that they’ll happily make that change for you.
However, the question remains: How do you find unlinked brand mentions in the first place?
Learn how to do that in our full guide to unlinked mentions.
4. Let the right people know about your content
People can’t link to content if they don’t know it exists.
That’s why you should make a conscious effort to tell people—the right people—about your content. But who are the “right” people?
They have two attributes:
- They are likely to be interested in your content;
- They have the power to link to you.
These people are often nicknamed the “linkerati.”
You can let them know about your content by performing blogger outreach.
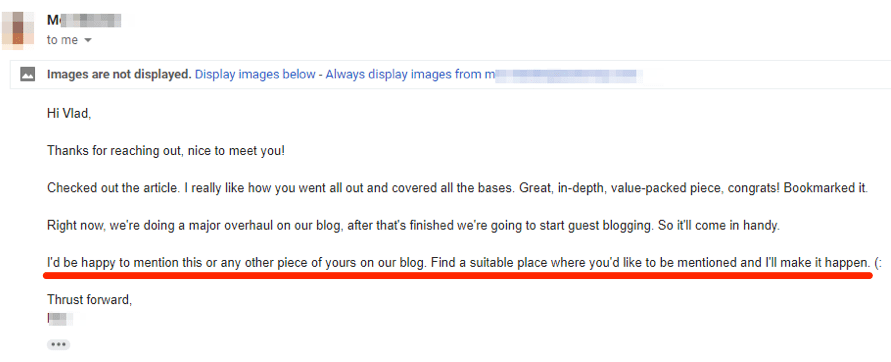
Does it work? Yes, it does. We do it all the time.
Here’s a reply from one of our recent campaigns:
We have a lot of resources related to link building on the Ahrefs Blog.