World Geography : Classification, Significance and Formation of Plateaus. ( UPSC )
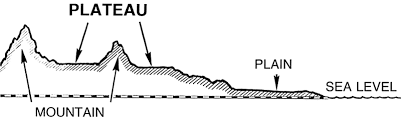
- A plateau is an elevated area with a more or less levelled land on its top.
- They are also called as high plains or tablelands.
- The plateaus cover about 18% of the earth’s land surface.
General characteristics of Plateaus
- Large area on its top.
- A steep slope on its sides
Classification of Plateaus

A- On the basis of Mode of Origin
- By exogenous forces
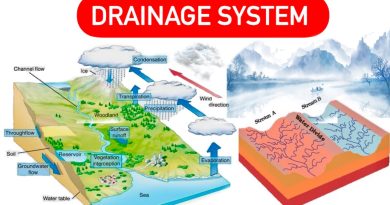
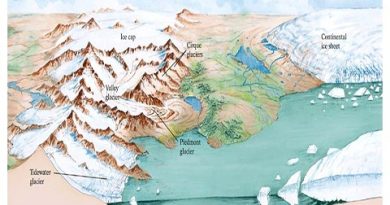
1.Glacial Plateau
- Through glacial erosion, mountainous areas are converted into flat plateaus.
- Plateau of Antarctica and Greenland, Garhwal plateau.
2. Plateau formed by Air
- The wind carries with it the deposition of fine particles of soil, which over time forms the plateau.
- Potwar Plateau
3. Alluvial Plateau
- Due to the deposition of sediments by rivers, the landmass keeps rising, customary plateaus are formed.
- Vindhya Plateau, Cherrapunji Plateau.
Formed by Endogenous Forces
1. Diastrophic Plateau
- Plateaus are formed due to uplift in the crust.
- Tibetan plateau, formed by the rise of the middle body at the time of mountain formation.
2. Volcanic Plateau
- A volcanic plateau is a plateau produced by volcanic activity.
- Ex- Columbia Plateau.
- There are two main types: lava plateaus and pyroclastic plateaus.
a) Lava Plateaus
- Lava plateaus are formed by highly fluid basaltic lava during numerous successive eruptions through numerous vents without violent explosions.
b) Pyroclastic Volcanic Plateaus
- Pyroclastic volcanic plateaus are produced by massive pyroclastic flows and they are underlain by pyroclastic rocks.
B- On the basis of their Geographical location
1. Intermontane Plateaus
- The plateaus which are bordering the mountain ranges (generally fold mountains) or are partly or fully enclosed within them.
- Intermontane plateaus are the highest in the world.
- They have nearly horizontal rock layers which are raised to very heights by vertical movements of the earth.
- Plateau of Tibet, Peru, Plateau of Bolibia, Plateau of Mexico.
2. Piedmont Plateaus
- Plateaus which is situated at the foot of a mountain and is locked on the other side by a plain or a sea/ ocean.
- They are also called as Plateaus of denudation as the areas once were high to the level of mountains, have now been reduced to the foot level of the mountain by various agents of erosion.
- Its formation is occurs due to the upliftment during the formation of mountains.
- Patagonia Plateau, Piedmont Plateau , Malwa Plateau.
3. Continental Plateau
- They are away from mountains but surrounded by oceanic beaches or plains.
- Are also known as Plateaus of Accumulation.
- Plateau of Maharashtra.
4. Coastal Plateau
- Plateaus located near sea coasts.
- Coromandal
The Economic significance of Plateaus
1. A storehouse of Minerals
- Most of the minerals in the world are found in plateaus.
- The extraction of minerals in plateaus is relatively easier on plateaus than mountains.
- The major portions of industrial raw materials are obtained from plateaus.
- Ex- Gold from the plateau of Western Australia ,copper, diamond and gold from the plateaus of Africa and coal, iron, manganese and mica from the Chottanagpur Plateau in India.
2. Generation of hydel-power
- The edges of plateaus form waterfalls which provide ideal sites for generating hydel power.
3. Cool Climate
- The higher parts of the plateaus even in tropical and sub-tropical regions have a cool climate.
4. Animal rearing and agriculture
- Plateaus have large grassland areas suitable for animal rearing especially sheep, goat, and cattle.
- The lava plateaus when compared to other plateaus are richer in minerals and hence used for agriculture as the soil is very fertile.