World Geography : Classification and Significance of Plains. ( UPSC )
- A plain is nothing but a low-lying relatively flat land surface with very gentle slope and minimum local relief.
- About 55% of the earth’s land surface is occupied by plains.

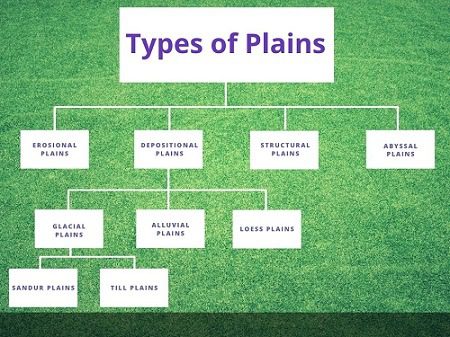
Classification of Plains
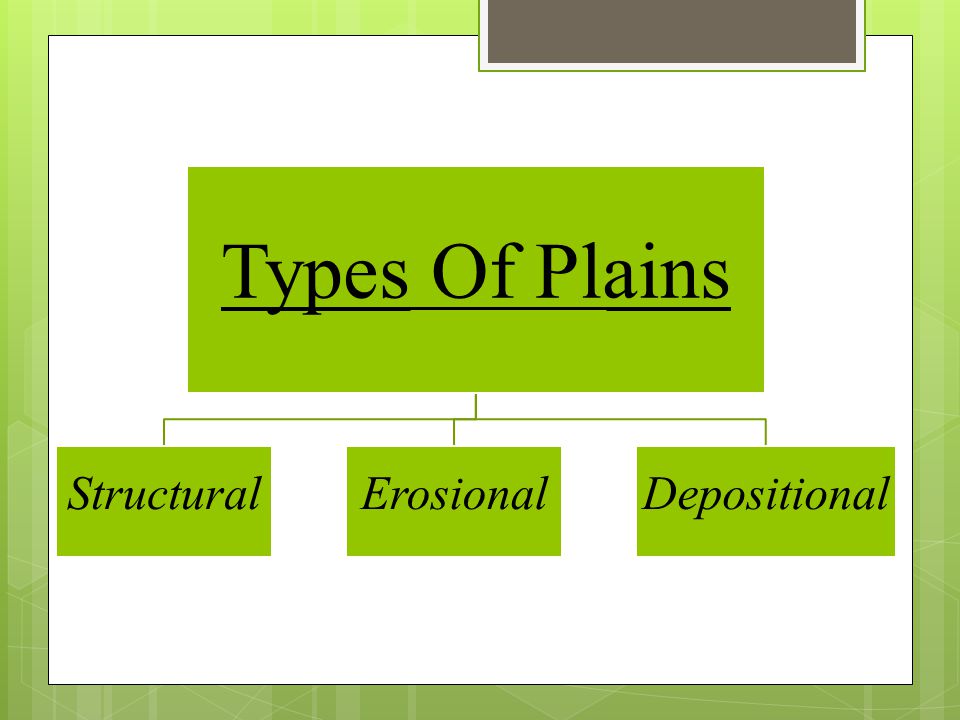
On the basis of their mode of formation, plains can be classified as:
- Structural Plains
- Erosional Plains
- Depositional Plains
1. Structural Plain
- These plains are mainly formed by the upliftment of a part of the sea floor or continental shelf.
- They are located on the borders of almost all the major continents.
- The structural plains may also be formed by the subsidence of areas.
- Examples – Russian Platforms, Great plains of USA & Central lowlands of Australia.
2. Erosional Plain
- The erosional forces remove the disparities of the land by erosion and convert the land area into a flat and shapeless plain.
Erosion by the River
- Erode the high landmass and converts it into peniplain.
- The resistant rocks found everywhere are called Monadnac.
Erosion by Glacier
- Glacier erosion converts the highland section into a flat but relief plain.
Erosion by Wind
- Rocks in arid and semi-arid regions get disintegrated by weathering and get converted into particles.
- The winds carry these particles with them, due to which the rocky part gets eroded and turns into a plain.
- The resistant rocks found are called Inselberg.
- The plain formed on the mountain slopes is called pediplain.
Karst Plain
- Conversion of lime rocks into plain due to erosion by underground water.
3. Depositional Plains
- Various factors of erosion form the plains through the deposition process.
1. Alluvial Cone
- Rivers descending from the hill slopes form alluvial cones / alluvial fans on the foothills.
- This ground, made up of a pile of big pieces, is called Bhabar.
2. Flood Plain
- During floods, rivers flow over the embankments and form a flood plain, which has alluvial/trembling or alluvial soil.
3. Delta Plains
- When the rivers fall into the oceans, due to the slowdown in their velocity, they left deposition near the mouth, a triangular flat plain is formed which is called the delta plain.
4. Lacustrine Plain (Lake Plain)
- Plains formed due to deposition by rivers falling into lakes or drying up of lakes.
5. Lava Plains
- Plains formed by liquid lava emanating from a volcanic eruption.
6. Loess Plains
- By depositing sand particles wind forms the plain.
The Economic Significance of Plains
1. Fertile Soil
- The plains generally have deep and fertile soil.
- As they have a flat surface, the means of irrigation can be easily developed.
- That is why plains are called as the ‘Food baskets of the world’.
2. The Growth of Industries
- The rich agricultural resources, especially of alluvial plains, have helped in the growth of agro-based industries.
- Since the plains are thickly populated, plenty of labor is available for the intense cultivation and for supplying the workforce for the industries.
3. Expansion of means of Transportation
- The flat surface of plains favours the building of roads, airports and laying down railway lines.
4. Centres of Civilizations
- Plains are centres of many civilizations.
5. Setting up of Cities and Towns
- Easy means of transportation on land and the growth of agriculture and industries in plains have resulted in the setting up and expansion of cities and towns.